Regulated expression of the centrosomal protein DdCP224 affects microtubule dynamics and reveals mechanisms for the control of supernumerary centrosome number
- PMID: 14517319
- PMCID: PMC207000
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-04-0242
Regulated expression of the centrosomal protein DdCP224 affects microtubule dynamics and reveals mechanisms for the control of supernumerary centrosome number
Abstract
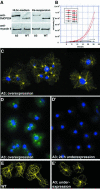
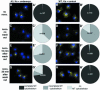
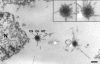
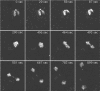
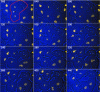
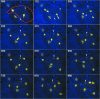
The Dictyostelium XMAP215 family member DdCP224 is involved in centrosome duplication and cytokinesis and is concentrated at the centrosome and microtubule tips. Herein, we have created a DdCP224 promoter replacement mutant that allows both over- and underexpression. Overexpression led to supernumerary microtubule-organizing centers and, independently, an increase of the number of multinuclear cells. Electron microscopy demonstrated that supernumerary microtubule-organizing centers represented bona fide centrosomes. Live cell imaging of DdCP224-green fluorescent protein mutants also expressing green fluorescent protein-histone2B as a DNA label revealed that supernumerary centrosomes were also competent of cell cycle-dependent duplication. In contrast, underexpression of DdCP224 inhibited cell growth, reduced the number and length of astral microtubules, and caused nocodazole hypersensitivity. Moreover, microtubule regrowth after nocodazole removal was dependent on DdCP224. Underexpression also resulted in a striking disappearance of supernumerary centrosomes and multinuclear cells caused by previous overexpression. We show for the first time by live cell observation that the number of supernumerary centrosomes can be reduced either by centrosome fusion (coalescence) or by the formation of cytoplasts containing supernumerary centrosomes during cytokinesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dictyostelium DdCP224 is a microtubule-associated protein and a permanent centrosomal resident involved in centrosome duplication.J Cell Sci. 2000 May;113 ( Pt 10):1747-58. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.10.1747. J Cell Sci. 2000. PMID: 10769206
-
Dictyostelium EB1 is a genuine centrosomal component required for proper spindle formation.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Jul;13(7):2301-10. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-01-0054. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12134070 Free PMC article.
-
Centrosomal microtubule plus end tracking proteins and their role in Dictyostelium cell dynamics.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2002;23(7-8):621-30. doi: 10.1023/a:1024450922609. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2002. PMID: 12952061 Review.
-
Dictyostelium LIS1 is a centrosomal protein required for microtubule/cell cortex interactions, nucleus/centrosome linkage, and actin dynamics.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Jun;16(6):2759-71. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-01-0069. Epub 2005 Mar 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15800059 Free PMC article.
-
MAPping the eukaryotic tree of life: structure, function, and evolution of the MAP215/Dis1 family of microtubule-associated proteins.Int Rev Cytol. 2004;239:179-272. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(04)39004-2. Int Rev Cytol. 2004. PMID: 15464854 Review.
Cited by
-
Rules of engagement: centrosome-nuclear connections in a closed mitotic system.Biol Open. 2012 Nov 15;1(11):1111-7. doi: 10.1242/bio.20122188. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Biol Open. 2012. PMID: 23213391 Free PMC article.
-
CDK5RAP2 Is an Essential Scaffolding Protein of the Corona of the Dictyostelium Centrosome.Cells. 2018 Apr 23;7(4):32. doi: 10.3390/cells7040032. Cells. 2018. PMID: 29690637 Free PMC article.
-
Dictyostelium Aurora kinase has properties of both Aurora A and Aurora B kinases.Eukaryot Cell. 2008 May;7(5):894-905. doi: 10.1128/EC.00422-07. Epub 2008 Mar 7. Eukaryot Cell. 2008. PMID: 18326585 Free PMC article.
-
CP55, a novel key component of centrosomal organization in Dictyostelium.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Nov;69(21):3651-64. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1040-3. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22744750 Free PMC article.
-
Mini spindles, the XMAP215 homologue, suppresses pausing of interphase microtubules in Drosophila.EMBO J. 2005 Apr 6;24(7):1387-96. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600629. Epub 2005 Mar 17. EMBO J. 2005. PMID: 15775959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brinkley, B.R. (2001). Managing the centrosome numbers game: from chaos to stability in cancer cell division. Trends Cell Biol. 11, 18–21. - PubMed
-
- Busson, S., Dujardin, D., Moreau, A., Dompierre, J., and DeMey, J.R. (1998). Dynein and dynactin are localized to astral microtubules and at cortical sites in mitotic epithelial cells. Curr. Biol. 8, 541–544. - PubMed
-
- Cassimeris, L., Gard, D., Tran, P.T., and Erickson, H.P. (2001). XMAP215 is a long thin molecule that does not increase microtubule stiffness. J. Cell Sci. 114, 3025–3033. - PubMed
-
- Charrasse, S., Mazel, M., Taviaux, S., Berta, P., Chow, T., and Larroque, C. (1995). Characterization of the cDNA and pattern of expression of a new gene over-expressed in human hepatomas and colonic tumors. Eur. J. Biochem. 234, 406–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

