Zinc fingers can act as Zn2+ sensors to regulate transcriptional activation domain function
- PMID: 14517251
- PMCID: PMC204467
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg484
Zinc fingers can act as Zn2+ sensors to regulate transcriptional activation domain function
Abstract
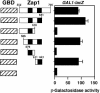
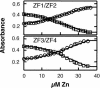
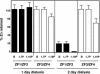
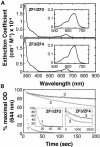
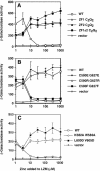
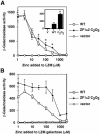
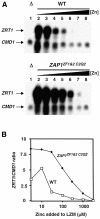
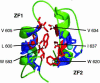
The yeast Zap1 transcription factor controls the expression of genes involved in zinc accumulation and storage. Zap1 is active in zinc-limited cells and repressed in replete cells. Zap1 has two activation domains, AD1 and AD2, which are both regulated by zinc. AD2 function was mapped to a region containing two Cys2His2 zinc fingers, ZF1 and ZF2, that are not involved in DNA binding. More detailed mapping placed AD2 almost precisely within the endpoints of ZF2, suggesting a role for these fingers in regulating activation domain function. Consistent with this hypothesis, ZF1 and ZF2 bound zinc in vitro but less stably than did zinc fingers involved in DNA binding. Furthermore, mutations predicted to disrupt zinc binding to ZF1 and/or ZF2 rendered AD2 constitutively active. Our results also indicate that the repressed form of AD2 requires an intramolecular interaction between ZF1 and ZF2. These studies suggest that these zinc fingers play an unprecedented role as zinc sensors to control activation domain function.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Solution structure of a Zap1 zinc-responsive domain provides insights into metalloregulatory transcriptional repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Mol Biol. 2006 Apr 7;357(4):1167-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Jan 24. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16483601
-
Zinc binding to a regulatory zinc-sensing domain monitored in vivo by using FRET.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jun 6;103(23):8674-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600928103. Epub 2006 May 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16720702 Free PMC article.
-
A dual role for zinc fingers in both DNA binding and zinc sensing by the Zap1 transcriptional activator.EMBO J. 2000 Jul 17;19(14):3704-13. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.14.3704. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 10899124 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc sensing and regulation in yeast model systems.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016 Dec 1;611:30-36. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2016.02.031. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016. PMID: 26940262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zinc'ing sensibly: controlling zinc homeostasis at the transcriptional level.Metallomics. 2014 Jul;6(7):1198-215. doi: 10.1039/c4mt00064a. Metallomics. 2014. PMID: 24722954 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of cation balance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2013 Mar;193(3):677-713. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.147207. Genetics. 2013. PMID: 23463800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aspergillus fumigatus survival in alkaline and extreme zinc-limiting environments relies on the induction of a zinc homeostasis system encoded by the zrfC and aspf2 genes.Eukaryot Cell. 2010 Mar;9(3):424-37. doi: 10.1128/EC.00348-09. Epub 2009 Dec 28. Eukaryot Cell. 2010. PMID: 20038606 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc Homeostasis in Platelet-Related Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 23;20(21):5258. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215258. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31652790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocyte-Specific Co-Delivery of Zinc Ions and Plasmid DNA by Lactosylated Poly(1-vinylimidazole) for Suppression of Insulin Receptor Internalization.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 4;13(12):2084. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13122084. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34959365 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular iron sensing by the direct binding of iron to regulators.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Mar 11;6:155. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00155. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 25815002 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Andrews G.K. (2001) Cellular zinc sensors: MTF-1 regulation of gene expression. Biometals, 14, 223–237. - PubMed
-
- Atar D., Backx,P.H., Appel,M.M., Gao,W.D. and Marban,E. (1995) Excitation–transcription coupling mediated by zinc influx through voltage-dependent calcium channels. J. Biol. Chem., 270, 2473–2477. - PubMed
-
- Berg J.M. and Godwin,H.A. (1997) Lessons from zinc binding peptides. Ann. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct., 26, 357–371. - PubMed
-
- Bird A.J., Evans-Galea,M., Blankman,E., Zhao,H., Luo,H., Winge,D.R. and Eide,D.J. (2000a) Mapping the DNA binding domain of the Zap1 zinc-responsive transcriptional activator. J. Biol. Chem., 275, 16160–16166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

