Members of the USF family of helix-loop-helix proteins bind DNA as homo- as well as heterodimers
- PMID: 1450663
- PMCID: PMC6057381
Members of the USF family of helix-loop-helix proteins bind DNA as homo- as well as heterodimers
Abstract
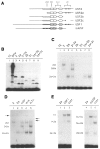
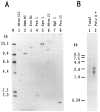
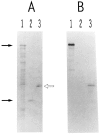
We have isolated human cDNA clones for USF2, a new member of the upstream stimulatory factor (USF) family of transcription factors. Analysis of these clones revealed the existence of highly conserved elements in the C terminal region of all USF proteins. These include the basic region, helix-loop-helix (HLH) motif, and, in the case of the human proteins, the C-terminal leucine repeat (LR). In addition, a highly conserved USF-specific domain is located immediately upstream of the basic region. Using in vitro translated proteins, we found that all members of the USF family bound DNA as dimers. The N-terminal portion of USF, including the USF-specific domain, was entirely dispensable for dimer formation and DNA-binding. However, deletion mutants of USF2 lacking the LR were deficient in DNA-binding activity. Interestingly, each of the USF proteins could form functional heterodimers with the other family members, including the sea urchin USF, which does not have a LR motif. This indicates that the conserved LR in human USF is not required for dimer formation, and influences only indirectly DNA-binding.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The adenovirus major late transcription factor USF is a member of the helix-loop-helix group of regulatory proteins and binds to DNA as a dimer.Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1730-40. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1730. Genes Dev. 1990. PMID: 2249772
-
Antiproliferative properties of the USF family of helix-loop-helix transcription factors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Feb 6;93(3):1308-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.3.1308. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8577760 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the leucine zipper in the kinetics of DNA binding by transcription factor USF.J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30694-700. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 7982989
-
Upstream stimulating factors: highly versatile stress-responsive transcription factors.Pigment Cell Res. 2005 Oct;18(5):337-48. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0749.2005.00262.x. Pigment Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 16162174 Review.
-
[USF as a key regulatory element of gene expression].Med Sci (Paris). 2006 Jan;22(1):62-7. doi: 10.1051/medsci/200622162. Med Sci (Paris). 2006. PMID: 16386222 Review. French.
Cited by
-
The Usf-1 transcription factor is a novel target for the stress-responsive p38 kinase and mediates UV-induced Tyrosinase expression.EMBO J. 2001 Sep 3;20(17):5022-31. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.17.5022. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11532965 Free PMC article.
-
Hematopoietic expression of HOXB4 is regulated in normal and leukemic stem cells through transcriptional activation of the HOXB4 promoter by upstream stimulating factor (USF)-1 and USF-2.J Exp Med. 2000 Nov 20;192(10):1479-90. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.10.1479. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 11085749 Free PMC article.
-
Human transcription factor USF stimulates transcription through the initiator elements of the HIV-1 and the Ad-ML promoters.EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):501-11. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05682.x. EMBO J. 1993. PMID: 8440240 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitous expression of the 43- and 44-kDa forms of transcription factor USF in mammalian cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 11;22(3):427-33. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.3.427. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994. PMID: 8127680 Free PMC article.
-
Upstream stimulatory factor activates the vasopressin promoter via multiple motifs, including a non-canonical E-box.Biochem J. 2003 Feb 1;369(Pt 3):549-61. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021176. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12403649 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beckmann H., Su L. K., and Kadesh T. (1990), Genes Dev 4, 177–179. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann H. and Kadesh T. (1991), Genes Dev 5, 1057–1066. - PubMed
-
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., and Eisenman R. N. (1990), Science 250, 1149–1151. - PubMed
-
- Blackwood E. M. and Eisenman R. N. (1991), Science 252, 1211–1217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
