Altered life cycle in Arabidopsis plants expressing PsUGT1, a UDP-glucuronosyltransferase-encoding gene from pea
- PMID: 12972656
- PMCID: PMC219030
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.103.026278
Altered life cycle in Arabidopsis plants expressing PsUGT1, a UDP-glucuronosyltransferase-encoding gene from pea
Abstract
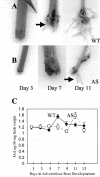
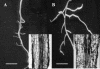
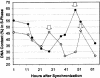
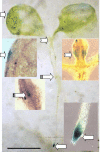
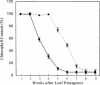
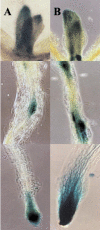
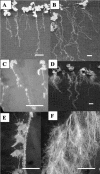
Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) and Arabidopsis were used as model systems to examine molecular mechanisms underlying developmental effects of a microsomal UDP-glucuronosyltransferase-encoding gene from pea (Pisum sativum; PsUGT1). Alfalfa expressing PsUGT1 antisense mRNA under the control of the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter exhibited delayed root emergence, reduced root growth, and increased lateral root development. The timing of root emergence in wild-type and antisense plants was correlated with the transient accumulation of auxin at the site of root emergence. Cell suspension cultures derived from the antisense alfalfa plants exhibited a delay in cell cycle from 24-h in the wild-type plants to 48-h in the antisense plants. PsUGT1::uidA was introduced into Arabidopsis to demonstrate that, as in alfalfa and pea, PsUGT1 expression occurs in regions of active cell division. This includes the root cap and root apical meristems, leaf primordia, tips of older leaves, and the transition zone between the hypocotyl and the root. Expression of PsUGT1::uidA colocalized with the expression of the auxin-responding reporter DR5::uidA. Co-expression of DR5::uidA in transgenic Arabidopsis lines expressing CaMV35S::PsUGT1 revealed that ectopic expression of CaMV35S::PsUGT1 is correlated with a change in endogenous auxin gradients in roots. Roots of ecotype Columbia expressing CaMV35S::PsUGT1 exhibited distinctive responses to exogenous naphthalene acetic acid. Completion of the life cycle occurred in 4 to 6 weeks compared with 6 to 7 weeks for wild-type Columbia. Inhibition of endogenous ethylene did not correct this early senescence phenotype.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Meristem-localized inducible expression of a UDP-glycosyltransferase gene is essential for growth and development in pea and alfalfa.Plant Cell. 1999 Dec;11(12):2303-15. doi: 10.1105/tpc.11.12.2303. Plant Cell. 1999. PMID: 10590160 Free PMC article.
-
The over-expression of an alfalfa RING-H2 gene induces pleiotropic effects on plant growth and development.Plant Mol Biol. 2003 May;52(1):121-33. doi: 10.1023/a:1023916701669. Plant Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12825694
-
Flavonoids: from cell cycle regulation to biotechnology.Biotechnol Lett. 2005 Mar;27(6):365-74. doi: 10.1007/s10529-005-1521-7. Biotechnol Lett. 2005. PMID: 15834800 Review.
-
SIZ1 regulation of phosphate starvation-induced root architecture remodeling involves the control of auxin accumulation.Plant Physiol. 2011 Feb;155(2):1000-12. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.165191. Epub 2010 Dec 14. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21156857 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic effects of suppressing deoxyhypusine synthase expression in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Mol Biol. 2003 Aug;52(6):1223-35. doi: 10.1023/b:plan.0000004332.80792.4d. Plant Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 14682621
Cited by
-
Characterization of Arabidopsis AtUGT85A and AtGUS gene families and their expression in rapidly dividing tissues.Genomics. 2007 Jul;90(1):143-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2007.03.014. Epub 2007 May 10. Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17498920 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and characterization of a glucosyltransferase from Crocus sativus stigmas involved in flavonoid glucosylation.BMC Plant Biol. 2009 Aug 20;9:109. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-9-109. BMC Plant Biol. 2009. PMID: 19695093 Free PMC article.
-
Inducible expression of Pisum sativum xyloglucan fucosyltransferase in the pea root cap meristem, and effects of antisense mRNA expression on root cap cell wall structural integrity.Plant Cell Rep. 2008 Jul;27(7):1125-35. doi: 10.1007/s00299-008-0530-0. Epub 2008 Mar 18. Plant Cell Rep. 2008. PMID: 18347802 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of cytokinin response in tomato leaves.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55090. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055090. Epub 2013 Jan 25. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23372818 Free PMC article.
-
Sad3 and sad4 are required for saponin biosynthesis and root development in oat.Plant Cell. 2008 Jan;20(1):201-12. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.056531. Epub 2008 Jan 18. Plant Cell. 2008. PMID: 18203919 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barlow PW (1975) The root cap. In JG Torrey, DT Clarkson, eds, The Development and Function of Roots. Academic Press, London, pp 21–54
-
- Barlow PW (2003) The root cap. J Plant Growth Regul (in press)
-
- Benjamins R, Quint A, Weijers D, Hooykaas P, Offringa R (2001) The PINOID protein kinase regulates organ development in Arabidopsis by enhancing polar auxin transport. Development 128: 4057–4067 - PubMed
-
- Bennett MJ, Marchant A, Green HG, May ST, Ward SP, Millner PA, Walker AR, Schultz B, Feldmann KA (1996) Arabidopsis AUX1 gene: a permease-like regulator of root gravitropism. Science 273: 948–950 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

