Study on relationship between expression level and molecular conformations of gene drugs targeting to hepatoma cells in vitro
- PMID: 12970883
- PMCID: PMC4656651
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.1954
Study on relationship between expression level and molecular conformations of gene drugs targeting to hepatoma cells in vitro
Abstract
Aim: To increase exogenous gene expression level by modulating molecular conformations of targeting gene drugs.
Methods: The full length cDNAs of both P(40) and P(35) subunits of human interleukin 12 were amplified through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and cloned into eukaryotic expressing vectors pcDNA3.1(+/-) to construct plasmids of P(+)/IL-12, P(+)/P(40) and P(-)/P(35). These plasmids were combined with ASOR-PLL to form two targeting gene drugs [ASOR-PLL-P(+)/IL-12 and ASOR-PLL-P(+)/P(40) + ASOR-PLL-P(-)/P(35)] in optimal ratios. The conformations of these two drugs at various concentrations adjuvant were examined under electron microscope (EM) and the drugs were transfected into HepG2 (ASGr+) cells. Semi-quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed with total RNA extracted from the transfected cells to determine the hIL12 mRNA transcript level. The hIL12 protein in the cultured supernatant was measured with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) 48 hours after transfection.
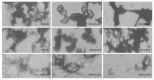
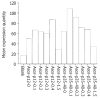
Results: Targeting gene drugs, whose structures were granular and circle-like and diameters ranged from 25 nm to 150 nm, had the highest hIL-12 expression level. The hIL-12 expression level in the group co-transfected with ASOR-PLL-P(+)/P(40) and ASOR-PLL-P(-)/P(35) was higher than that of ASOR-PLL-P(+)/IL-12 transfected group.
Conclusion: The molecular conformations of targeting gene drugs play an important role in exogenous gene expression level, the best structures are granular and circle-like and their diameters range from 25 nm to 150 nm. The sizes and linking styles of exogenous genes also have some effects on their expression level.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modulation of the molecular conformation of a hepatocyte-targeting gene drug in order to improve its expression efficiency in vitro.Chin J Dig Dis. 2005;6(1):37-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-9573.2005.00186.x. Chin J Dig Dis. 2005. PMID: 15667557
-
[Construction of double-subunit co-expression eukaryotic vector of human interleukin 12].Hunan Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2003 Aug;28(4):338-42. Hunan Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2003. PMID: 14653112 Chinese.
-
[PreC/C gene-targeting RNA interference suppresses hepatitis B virus replication and expression in human hepatoma cells].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012 Mar 20;92(11):768-72. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22781359 Chinese.
-
[Construction, expression and immunogenicity study of a chimeric MS/hIL-12 eukaryotic expression plasmid].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2006 Apr;29(4):261-5. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16750044 Chinese.
-
[Immunogenicity of chimeric gene vaccine Mtb8.4/hIL12].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006 Sep;22(5):597-600. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16948904 Chinese.
References
-
- Schuster MJ, Wu GY. Gene therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: progress but many stones yet unturned! Gastroenterology. 1997;112:656–659. - PubMed
-
- Ruiz J, Qian C, Prieto J. Gene therapy of liver tumors: principles and applications. Digestion. 1998;59 Suppl 2:92–96. - PubMed
-
- Zabner J, Fasbender AJ, Moninger T, Poellinger KA, Welsh MJ. Cellular and molecular barriers to gene transfer by a cationic lipid. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:18997–19007. - PubMed
-
- Mitry RR, Mansour MR, Havlík R, Habib NA. Gene therapy for liver tumours. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2000;465:193–205. - PubMed
-
- Han J, Il Yeom Y. Specific gene transfer mediated by galactosylated poly-L-lysine into hepatoma cells. Int J Pharm. 2000;202:151–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

