A missense mutation in the mouse Col2a1 gene causes spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita, hearing loss, and retinoschisis
- PMID: 12968670
- PMCID: PMC2862909
- DOI: 10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.9.1612
A missense mutation in the mouse Col2a1 gene causes spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita, hearing loss, and retinoschisis
Erratum in
- J Bone Miner Res. 2007 Dec;22(12):2011
Abstract
A missense mutation in the mouse Col2a1 gene has been discovered, resulting in a mouse phenotype with similarities to human spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia (SED) congenita. In addition, SED patients have been identified with a similar molecular mutation in human COL2A1. This mouse model offers a useful tool for molecular and biological studies of bone development and pathology.
Introduction: A new mouse autosomal recessive mutation has been discovered and named spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita (gene symbol sedc).
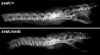
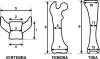
Materials and methods: Homozygous sedc mice can be identified at birth by their small size and shortened trunk. Adults have shortened noses, dysplastic vertebrae, femora, and tibias, plus retinoschisis and hearing loss. The mutation was mapped to Chr15, and Col2a1 was identified as a candidate gene.
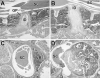
Results: Sequence analyses revealed that the affected gene is Col2a1, which has a missense mutation at exon 48 causing an amino acid change of arginine to cysteine at position 1417. Two human patients with spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia (SED) congenita have been reported with the same amino acid substitution at position 789 in the human COL2A1 gene.
Conclusions: Thus, sedc/sedc mice provide a valuable model of human SED congenita with molecular and phenotypic homology. Further biochemical analyses, molecular modeling, and cell culture studies using sedc/sedc mice could provide insight into mechanisms of skeletal development dependent on Col2a1 and its role in fibril formation and cartilage template organization.
Figures

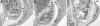

Similar articles
-
A mouse model for spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita with secondary osteoarthritis due to a Col2a1 mutation.J Bone Miner Res. 2012 Feb;27(2):413-28. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.547. J Bone Miner Res. 2012. PMID: 22028304
-
A novel COL2A1 mutation causing spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita in a Chinese family.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Apr;35(4):e23728. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23728. Epub 2021 Feb 16. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 33590889 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mutation in the COL2A1 gene in a Chinese family with Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita.Joint Bone Spine. 2014 Jan;81(1):86-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2013.06.010. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Joint Bone Spine. 2014. PMID: 23932928
-
Novel COL2A1 mutations causing spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita in three unrelated Chinese families.Eur Spine J. 2016 Sep;25(9):2967-74. doi: 10.1007/s00586-016-4559-4. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Eur Spine J. 2016. PMID: 27059630 Review.
-
A novel mutation in the COL2A1 gene in a patient with Stickler syndrome type 1: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2017 Aug 26;11(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s13256-017-1396-y. J Med Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28841907 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Persistence of intracellular and extracellular changes after incompletely suppressing expression of the R789C (p.R989C) and R992C (p.R1192C) collagen II mutants.Hum Mutat. 2011 Jul;32(7):794-805. doi: 10.1002/humu.21506. Epub 2011 May 5. Hum Mutat. 2011. PMID: 21472893 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and characterization of spontaneous mouse models of craniofacial dysmorphology.Dev Biol. 2016 Jul 15;415(2):216-227. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.07.023. Epub 2015 Jul 31. Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26234751 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress in chondrodysplasias caused by mutations in collagen types II and X.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2016 Nov;21(6):943-958. doi: 10.1007/s12192-016-0719-z. Epub 2016 Aug 15. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2016. PMID: 27523816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CHD7 regulates craniofacial cartilage development via controlling HTR2B expression.J Bone Miner Res. 2024 May 2;39(4):498-512. doi: 10.1093/jbmr/zjae024. J Bone Miner Res. 2024. PMID: 38477756 Free PMC article.
-
Novel NPR2 Gene Mutations Affect Chondrocytes Function via ER Stress in Short Stature.Cells. 2022 Apr 8;11(8):1265. doi: 10.3390/cells11081265. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35455946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vikkula M, Metsaranta M, Ala-Kokko L. Type II collagen mutations in rare and common cartilate diseases. Ann Med. 1994;26:107–114. - PubMed
-
- Whyte MP. Chondrodystrophies and mucopolysaccharidoses. In: Favus MJ, editor. Primer on the Metabolic Bone Diseases and Disorders of Mineral Metabolism. 4th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 1999. pp. 289–393.
-
- Francomono C, Liberfarb R, Hirose T, Maumenee I, Streeten E, Meyers D, Pyeritz R. The Stickler syndrome: Evidence for close linkage to the structural gene for type II collagen. Genomics. 1987;1:293–296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RR01183/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA034196-169007/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- EY07758/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019698/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA034196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DE013078/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DC004376-01A1/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- DE13078/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P40 RR001183/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- CA34186/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY007758/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY007758-11/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DE013078-01/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P40 RR001183-22/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019698-02/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG19698/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

