Repression of Smad transcriptional activity by PIASy, an inhibitor of activated STAT
- PMID: 12904571
- PMCID: PMC187844
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1733973100
Repression of Smad transcriptional activity by PIASy, an inhibitor of activated STAT
Abstract
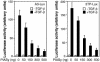
Smad proteins mediate transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta)-inducible transcriptional responses. Protein inhibitor of activated signal transducer and activator of transcription (PIAS) represents a family of proteins that inhibits signal transducer and activator of transcription and also regulates other transcriptional responses. In an effort to identify Smad-interacting proteins by a yeast three-hybrid screen with Smad3 and Smad4 as baits, we identified PIASy, a member of the PIAS family. In yeast, PIASy interacts strongly with Smad4 and also with receptor-regulated Smads. In mammalian cells, PIASy binds most strongly with Smad3 and also associates with other receptor-regulated Smads and Smad4. The interaction between Smad3 and PIASy is increased in the presence of TGF-beta and occurs through the C-terminal domain of Smad3. Moreover, Smad3, Smad4, and PIASy can form a ternary complex. PIASy does not inhibit Smad complex binding to DNA, but it represses Smad transcriptional activity. Interestingly, conditional overexpression of PIASy selectively inhibits a subset of endogenous TGF-beta-responsive genes, which includes the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p15, and the plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. We further show that PIASy can interact constitutively with histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and that addition of HDAC inhibitor trichostatin A (TSA) can prevent the inhibitory function of PIASy. Taken together, our studies indicate that PIASy can inhibit TGF-beta/Smad transcriptional responses through interactions with Smad proteins and HDAC.
Figures



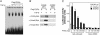
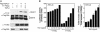
Similar articles
-
Activation of Smad transcriptional activity by protein inhibitor of activated STAT3 (PIAS3).Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jan 6;101(1):99-104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307598100. Epub 2003 Dec 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14691252 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of transforming growth factor-beta signaling by protein inhibitor of activated STAT, PIASy through Smad3.J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 5;278(36):34253-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304961200. Epub 2003 Jun 18. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12815042
-
Sumoylation of Smad4, the common Smad mediator of transforming growth factor-beta family signaling.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jul 25;278(30):27853-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301755200. Epub 2003 May 11. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12740389
-
Tumor suppressor Smad4 is a transforming growth factor beta-inducible DNA binding protein.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Dec;17(12):7019-28. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.12.7019. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9372933 Free PMC article.
-
The Smads: transcriptional regulation and mouse models.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000 Mar-Jun;11(1-2):37-48. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(99)00027-1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000. PMID: 10708951 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-22 is a master regulator of bone morphogenetic protein-7/6 homeostasis in the kidney.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 20;288(51):36202-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.498634. Epub 2013 Oct 25. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24163368 Free PMC article.
-
To (TGF)beta or not to (TGF)beta: fine-tuning of Smad signaling via post-translational modifications.Cell Signal. 2008 Sep;20(9):1579-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.02.003. Epub 2008 Feb 15. Cell Signal. 2008. PMID: 18387785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PIASy represses CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta (C/EBPdelta) transcriptional activity by sequestering C/EBPdelta to the nuclear periphery.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jul 18;283(29):20137-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801307200. Epub 2008 May 12. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18477566 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Targeting the SUMO Pathway in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 31;13(17):4402. doi: 10.3390/cancers13174402. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34503213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin E3 ligase FIEL1 regulates fibrotic lung injury through SUMO-E3 ligase PIAS4.J Exp Med. 2016 May 30;213(6):1029-46. doi: 10.1084/jem.20151229. Epub 2016 May 9. J Exp Med. 2016. PMID: 27162139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Derynck, R., Zhang, Y. & Feng, X.-H. (1998) Cell 95, 737–740. - PubMed
-
- Attisano, L. & Wrana, J. L. (2000) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12, 235–243. - PubMed
-
- Shi, Y. & Massagué, J. (2003) Cell 113, 685–700. - PubMed
-
- Zawel, L., Dai, J., Buckhaults, P., Zhou, S., Kinzler, K., Vogelstein, B. & Kern, S. (1998) Mol. Cell 1, 611–617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

