Yeast recombination pathways triggered by topoisomerase II-mediated DNA breaks
- PMID: 12888496
- PMCID: PMC169887
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg497
Yeast recombination pathways triggered by topoisomerase II-mediated DNA breaks
Abstract
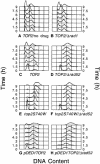
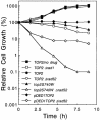
Topoisomerase II is a ubiquitous enzyme that removes knots and tangles from the genetic material by generating transient double-strand DNA breaks. While the enzyme cannot perform its essential cellular functions without cleaving DNA, this scission activity is inherently dangerous to chromosomal integrity. In fact, etoposide and other clinically important anticancer drugs kill cells by increasing levels of topoisomerase II-mediated DNA breaks. Cells rely heavily on recombination to repair double-strand DNA breaks, but the specific pathways used to repair topoisomerase II-generated DNA damage have not been defined. Therefore, Saccharomyces cerevisiae was used as a model system to delineate the recombination pathways that repair DNA breaks generated by topoisomerase II. Yeast cells that expressed wild-type or a drug-hypersensitive mutant topoisomerase II or overexpressed the wild-type enzyme were examined. Based on cytotoxicity and recombination induced by etoposide in different repair-deficient genetic backgrounds, double-strand DNA breaks generated by topoisomerase II appear to be repaired primarily by the single-strand invasion pathway of homologous recombination. Non-homologous end joining also was triggered by etoposide treatment, but this pathway was considerably less active than single-strand invasion and did not contribute significantly to cell survival in S.cerevisiae.
Figures


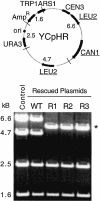
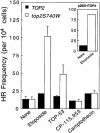

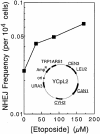
Similar articles
-
Roles of nonhomologous end-joining pathways in surviving topoisomerase II-mediated DNA damage.Mol Cancer Ther. 2006 Jun;5(6):1405-14. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0263. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006. PMID: 16818498
-
Mms22p protects Saccharomyces cerevisiae from DNA damage induced by topoisomerase II.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Feb 17;33(3):1021-30. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki246. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15718301 Free PMC article.
-
Etoposide, topoisomerase II and cancer.Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2005 Jul;5(4):363-72. doi: 10.2174/1568011054222364. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2005. PMID: 16101488 Review.
-
DNA topoisomerase II as the target for the anticancer drug TOP-53: mechanistic basis for drug action.Biochemistry. 2001 Jan 23;40(3):712-8. doi: 10.1021/bi0021838. Biochemistry. 2001. PMID: 11170388
-
The DNA cleavage reaction of topoisomerase II: wolf in sheep's clothing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Feb;37(3):738-48. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn937. Epub 2008 Nov 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19042970 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pleiotropic functions of EAPII/TTRAP/TDP2: cancer development, chemoresistance and beyond.Cell Cycle. 2011 Oct 1;10(19):3274-83. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.19.17763. Epub 2011 Oct 1. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 21926483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The evolutionary origin of man can be traced in the layers of defunct ancestral alpha satellites flanking the active centromeres of human chromosomes.PLoS Genet. 2009 Sep;5(9):e1000641. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000641. Epub 2009 Sep 11. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19749981 Free PMC article.
-
YNK1, the yeast homolog of human metastasis suppressor NM23, is required for repair of UV radiation- and etoposide-induced DNA damage.Mutat Res. 2009 Jan 15;660(1-2):74-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2008.09.015. Epub 2008 Oct 15. Mutat Res. 2009. PMID: 18983998 Free PMC article.
-
MRE11 facilitates the removal of human topoisomerase II complexes from genomic DNA.Biol Open. 2012 Sep 15;1(9):863-73. doi: 10.1242/bio.20121834. Epub 2012 Jul 11. Biol Open. 2012. PMID: 23213480 Free PMC article.
-
Rejuvenating the immune system in rheumatoid arthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009 Oct;5(10):583-8. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2009.180. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19798035 Review.
References
-
- Wang J.C. (1996) DNA topoisomerases. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 65, 635–692. - PubMed
-
- Burden D.A. and Osheroff,N. (1998) Mechanism of action of eukaryotic topoisomerase II and drugs targeted to the enzyme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1400, 139–154. - PubMed
-
- Nitiss J.L. (1998) Investigating the biological functions of DNA topoisomerases in eukaryotic cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1400, 63–81. - PubMed
-
- Wang J.C. (1998) Moving one DNA double helix through another by a type II DNA topoisomerase: the story of a simple molecular machine. Q. Rev. Biophys., 31, 107–144. - PubMed
-
- Fortune J.M. and Osheroff,N. (2000) Topoisomerase II as a target for anticancer drugs: when enzymes stop being nice. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol., 64, 221–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

