Prediction of lipoprotein signal peptides in Gram-negative bacteria
- PMID: 12876315
- PMCID: PMC2323952
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.0303703
Prediction of lipoprotein signal peptides in Gram-negative bacteria
Abstract
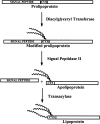
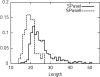
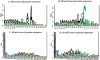
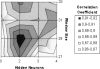
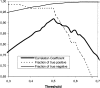
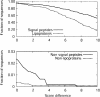
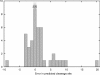
A method to predict lipoprotein signal peptides in Gram-negative Eubacteria, LipoP, has been developed. The hidden Markov model (HMM) was able to distinguish between lipoproteins (SPaseII-cleaved proteins), SPaseI-cleaved proteins, cytoplasmic proteins, and transmembrane proteins. This predictor was able to predict 96.8% of the lipoproteins correctly with only 0.3% false positives in a set of SPaseI-cleaved, cytoplasmic, and transmembrane proteins. The results obtained were significantly better than those of previously developed methods. Even though Gram-positive lipoprotein signal peptides differ from Gram-negatives, the HMM was able to identify 92.9% of the lipoproteins included in a Gram-positive test set. A genome search was carried out for 12 Gram-negative genomes and one Gram-positive genome. The results for Escherichia coli K12 were compared with new experimental data, and the predictions by the HMM agree well with the experimentally verified lipoproteins. A neural network-based predictor was developed for comparison, and it gave very similar results. LipoP is available as a Web server at www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/LipoP/.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prediction of lipoprotein signal peptides in Gram-positive bacteria with a Hidden Markov Model.J Proteome Res. 2008 Dec;7(12):5082-93. doi: 10.1021/pr800162c. J Proteome Res. 2008. PMID: 19367716
-
Genome-wide protein localization prediction strategies for gram negative bacteria.BMC Genomics. 2011 Jun 15;12 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-S1-S1. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21810203 Free PMC article.
-
Pattern searches for the identification of putative lipoprotein genes in Gram-positive bacterial genomes.Microbiology (Reading). 2002 Jul;148(Pt 7):2065-2077. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-7-2065. Microbiology (Reading). 2002. PMID: 12101295
-
Sorting of lipoproteins to the outer membrane in E. coli.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Nov 11;1694(1-3):IN1-9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15672528 Review.
-
Biogenesis of outer membranes in Gram-negative bacteria.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2009 Mar 23;73(3):465-73. doi: 10.1271/bbb.80778. Epub 2009 Mar 7. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19270402 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome Sequence of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Bacteriophage MG40.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2020 Sep 10;9(37):e00905-20. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00905-20. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2020. PMID: 32912919 Free PMC article.
-
An ultrasensitive nanofiber-based assay for enzymatic hydrolysis and deep-sea microbial degradation of cellulose.iScience. 2022 Jul 30;25(8):104732. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104732. eCollection 2022 Aug 19. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36039358 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Mhp462 antibody induced by natural infection but not in vitro culture of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae.Heliyon. 2020 Aug 31;6(8):e04832. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04832. eCollection 2020 Aug. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32923730 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical characterization of a SusD-like protein involved in β-1,3-glucan utilization by an uncultured cow rumen Bacteroides.mSphere. 2024 Aug 28;9(8):e0027824. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00278-24. Epub 2024 Jul 16. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 39012103 Free PMC article.
-
Features of two proteins of Leptospira interrogans with potential role in host-pathogen interactions.BMC Microbiol. 2012 Mar 30;12:50. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-50. BMC Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22463075 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braun, V. and Wu, H.C. 1994. Lipoproteins, structure, function, biosynthesis, and a model for protein export. In Bacterial cell wall (eds. J.M. Ghuysen and R. Hakenbeck), pp. 319–341. Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

