The antitumor effects of IFN-alpha are abrogated in a STAT1-deficient mouse
- PMID: 12865406
- PMCID: PMC164283
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI16603
The antitumor effects of IFN-alpha are abrogated in a STAT1-deficient mouse
Abstract
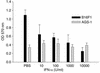
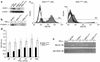
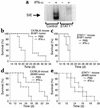
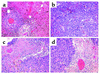
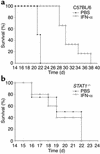
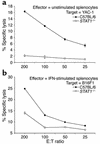
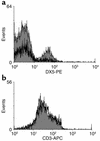
IFN-alpha activates the signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) family of proteins; however, it is unknown whether IFN-alpha exerts its antitumor actions primarily through a direct effect on malignant cells or by stimulating the immune system. To investigate the contribution of STAT1 signaling within the tumor, we generated a STAT1-deficient melanoma cell line, AGS-1. We reconstituted STAT1 into AGS-1 cells by retroviral gene transfer. The resulting cell line (AGS-1STAT1) showed normal regulation of IFN-alpha-stimulated genes (e.g., H2k, ISG-54) as compared with AGS-1 cells infected with the empty vector (AGS-1MSCV). However, mice challenged with the AGS-1, AGS-1STAT1, and AGS-1MSCV cell lines exhibited nearly identical survival in response to IFN-alpha treatment, indicating that restored STAT1 signaling within the tumor did not augment the antitumor activity of IFN-alpha. In contrast, STAT1-/- mice could not utilize exogenous IFN-alpha to inhibit the growth of STAT1+/+ melanoma cells in either an intraperitoneal tumor model or in the adjuvant setting. The survival of tumor-bearing STAT1-/- mice was identical regardless of treatment (IFN-alpha or PBS). Additional cell depletion studies demonstrated that NK cells mediated the antitumor effects of IFN-alpha. Thus, STAT1-mediated gene regulation within immune effectors was necessary for mediating the antitumor effects of IFN-alpha in this experimental system.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The antitumor effects of interferon-alpha are maintained in mice challenged with a STAT1-deficient murine melanoma cell line.J Surg Res. 2004 Jan;116(1):129-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2003.09.005. J Surg Res. 2004. PMID: 14732359
-
Multiparametric flow cytometric analysis of inter-patient variation in STAT1 phosphorylation following interferon Alfa immunotherapy.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004 Sep 1;96(17):1331-42. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djh252. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004. PMID: 15339971
-
Interferon-alpha-induced activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription proteins in malignant melanoma.Clin Cancer Res. 1998 Sep;4(9):2219-28. Clin Cancer Res. 1998. PMID: 9748142
-
Interferon alpha and CPG oligodeoxynucleotides elicit additive immunostimulatory and antitumor effects.Surgery. 2006 Aug;140(2):297-306. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2006.05.005. Surgery. 2006. PMID: 16904983
-
Interferon-alpha in tumor immunity and immunotherapy.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002 Apr;13(2):119-34. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(01)00022-3. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002. PMID: 11900988 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation mechanisms of natural killer cells during influenza virus infection.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51858. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051858. Epub 2012 Dec 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300570 Free PMC article.
-
Direct and indirect anti-leukemic properties of activity-on-target interferons for the treatment of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Haematologica. 2022 Jun 1;107(6):1448-1453. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2021.278913. Haematologica. 2022. PMID: 34647441 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Stat1 is an inducible transcriptional repressor of neural stem cells self-renewal program during neuroinflammation.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Aug 16;17:1156802. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1156802. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37663126 Free PMC article.
-
STAT1 and pathogens, not a friendly relationship.Biochimie. 2010 May;92(5):425-44. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2010.02.009. Epub 2010 Feb 13. Biochimie. 2010. PMID: 20159032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VEGF secretion is inhibited by interferon-alpha in several melanoma cell lines.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2008 Sep;28(9):553-61. doi: 10.1089/jir.2008.0118. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2008. PMID: 18771339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kirkwood JM, Ibrahim JG, Sondak VK, Ernstoff MS, Ross M. Interferon alfa-2a for melanoma metastases. Lancet. 2002;359:978–979. - PubMed
-
- Belardelli F, Ferrantini M, Proietti E, Kirkwood JM. Interferon-alpha in tumor immunity and immunotherapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002;13:119–134. - PubMed
-
- Kirkwood JM, et al. High- and low-dose interferon alfa-2b in high-risk melanoma: first analysis of intergroup trial E1690/S9111/C9190. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000;18:2444–2458. - PubMed
-
- Agarwala SS, Kirkwood JM. Potential uses of interferon alpha 2 as adjuvant therapy in cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 1995;2:365–371. - PubMed
-
- Biron CA. Interferons alpha and beta as immune regulators — a new look. Immunity. 2001;14:661–664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

