Changes in intracellular calcium and glutathione in astrocytes as the primary mechanism of amyloid neurotoxicity
- PMID: 12832532
- PMCID: PMC6741151
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-12-05088.2003
Changes in intracellular calcium and glutathione in astrocytes as the primary mechanism of amyloid neurotoxicity
Abstract
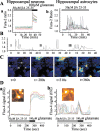
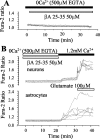
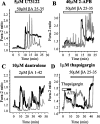
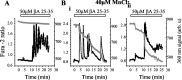
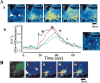
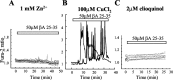
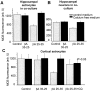
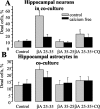
Although the accumulation of the neurotoxic peptide beta amyloid (betaA) in the CNS is a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease, the mechanism of betaA neurotoxicity remains controversial. In cultures of mixed neurons and astrocytes, we found that both the full-length peptide betaA (1-42) and the neurotoxic fragment (25-35) caused sporadic cytoplasmic calcium [intracellular calcium ([Ca2+]c)] signals in astrocytes that continued for hours, whereas adjacent neurons were completely unaffected. Nevertheless, after 24 hr, although astrocyte cell death was marginally increased, approximately 50% of the neurons had died. The [Ca2+]c signal was entirely dependent on Ca2+ influx and was blocked by zinc and by clioquinol, a heavy-metal chelator that is neuroprotective in models of Alzheimer's disease. Neuronal death was associated with Ca2+-dependent glutathione depletion in both astrocytes and neurons. Thus, astrocytes appear to be the primary target of betaA, whereas the neurotoxicity reflects the neuronal dependence on astrocytes for antioxidant support.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Membrane cholesterol content plays a key role in the neurotoxicity of β-amyloid: implications for Alzheimer's disease.Aging Cell. 2011 Aug;10(4):595-603. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00685.x. Epub 2011 Apr 11. Aging Cell. 2011. PMID: 21332922
-
Mechanism of neuroprotection of melatonin against beta-amyloid neurotoxicity.Neuroscience. 2011 Apr 28;180:229-37. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.02.045. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21354274
-
Beta-amyloid peptides induce mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in astrocytes and death of neurons through activation of NADPH oxidase.J Neurosci. 2004 Jan 14;24(2):565-75. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4042-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 14724257 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium signals induced by amyloid beta peptide and their consequences in neurons and astrocytes in culture.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Dec 6;1742(1-3):81-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.09.006. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15590058 Review.
-
The role of an astrocytic NADPH oxidase in the neurotoxicity of amyloid beta peptides.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005 Dec 29;360(1464):2309-14. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1766. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2005. PMID: 16321801 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction of Oxidative Stress and Misfolded Proteins in the Mechanism of Neurodegeneration.Life (Basel). 2020 Jun 30;10(7):101. doi: 10.3390/life10070101. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32629809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human stem cell-derived astrocytes and their application to studying Nrf2-mediated neuroprotective pathways and therapeutics in neurodegeneration.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Apr;75(4):907-18. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12022. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23126226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astrocytes in neurodegenerative disease.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Apr 15;7(6):a020628. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a020628. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 25877220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary cultures of astrocytes: their value in understanding astrocytes in health and disease.Neurochem Res. 2012 Nov;37(11):2569-88. doi: 10.1007/s11064-012-0868-0. Epub 2012 Aug 28. Neurochem Res. 2012. PMID: 22926576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of ginkgolide K on calcium channel activity in Alzheimer's disease.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jun;23(6):426. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11353. Epub 2022 May 5. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35607377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atwood CS, Moir RD, Huang X, Scarpa RC, Bacarra NM, Romano DM, Hartshorn MA, Tanzi RE, Bush AI ( 1998) Dramatic aggregation of Alzheimer Aβ by Cu(II) is induced by conditions representing physiological acidosis. J Biol Chem 273: 12817–12826. - PubMed
-
- Behl C, Davis JB, Lesley R, Schubert D ( 1994) Hydrogen peroxide mediates amyloid β protein toxicity. Cell 77: 817–822. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard BJ, Konopka G, Russell M, Ingram VM ( 1997) Mechanism and prevention of neurotoxicity caused by β-amyloid peptides: relation to Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 776: 40–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
