Mek2 is dispensable for mouse growth and development
- PMID: 12832465
- PMCID: PMC162209
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.14.4778-4787.2003
Mek2 is dispensable for mouse growth and development
Abstract
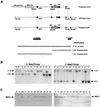
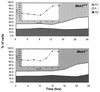
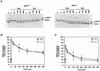
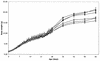
MEK is a dual-specificity kinase that activates the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase upon agonist binding to receptors. The ERK/MAP kinase cascade is involved in cell fate determination in many organisms. In mammals, this pathway is proposed to regulate cell growth and differentiation. Genetic studies have shown that although a single Mek gene is present in Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila melanogaster, and Xenopus laevis, two Mek homologs, Mek1 and Mek2, are present in the mammalian cascade. The inactivation of the Mek1 gene leads to embryonic lethality and has revealed the unique role played by Mek1 during embryogenesis. To investigate the biological function of the second homolog, we have generated mice deficient in Mek2 function. Mek2 mutant mice are viable and fertile, and they do not present flagrant morphological alteration. Although several components of the ERK/MAP kinase cascade have been implicated in thymocyte development, no such involvement was observed for MEK2, which appears to be nonessential for thymocyte differentiation and T-cell-receptor-induced proliferation and apoptosis. Altogether, our findings demonstrate that MEK2 is not necessary for the normal development of the embryo and T-cell lineages, suggesting that the loss of MEK2 can be compensated for by MEK1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Embryonic death of Mek1-deficient mice reveals a role for this kinase in angiogenesis in the labyrinthine region of the placenta.Curr Biol. 1999 Apr 8;9(7):369-72. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80164-x. Curr Biol. 1999. PMID: 10209122
-
Differential regulation of mitogen-activated protein/ERK kinase (MEK)1 and MEK2 and activation by a Ras-independent mechanism.Mol Endocrinol. 1997 Oct;11(11):1618-25. doi: 10.1210/mend.11.11.0010. Mol Endocrinol. 1997. PMID: 9328344
-
Cloning and characterization of two distinct human extracellular signal-regulated kinase activator kinases, MEK1 and MEK2.J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11435-9. J Biol Chem. 1993. PMID: 8388392
-
Regulation of the ERK subgroup of MAP kinase cascades through G protein-coupled receptors.Cell Signal. 1997 Aug;9(5):337-51. doi: 10.1016/s0898-6568(96)00191-x. Cell Signal. 1997. PMID: 9376213 Review.
-
Implication of MEK1 and MEK2 in the establishment of the blood-placenta barrier during placentogenesis in mouse.Reprod Biomed Online. 2012 Jul;25(1):58-67. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2012.02.012. Epub 2012 Mar 3. Reprod Biomed Online. 2012. PMID: 22561024 Review.
Cited by
-
ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway Activated by EGF Promotes Proliferation, Transdifferentiation, and Migration of Cultured Primary Newborn Rat Lung Fibroblasts.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Oct 5;2020:7176169. doi: 10.1155/2020/7176169. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33083482 Free PMC article.
-
IQGAP1 is a scaffold for mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Sep;25(18):7940-52. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.18.7940-7952.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16135787 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative whole-genome transcriptome analysis in renal cell populations reveals high tissue specificity of MAPK/ERK targets in embryonic kidney.BMC Biol. 2022 May 13;20(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12915-022-01309-z. BMC Biol. 2022. PMID: 35550069 Free PMC article.
-
Phase transition specified by a binary code patterns the vertebrate eye cup.Sci Adv. 2021 Nov 12;7(46):eabj9846. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abj9846. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 34757798 Free PMC article.
-
Specific functions for ERK/MAPK signaling during PNS development.Neuron. 2011 Jan 13;69(1):91-105. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.12.003. Neuron. 2011. PMID: 21220101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharya, U., A. Mallabiabarrena, J. K. Acharya, and V. Malhotra. 1998. Signaling via mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK1) is required for Golgi fragmentation during mitosis. Cell 92:183-192. - PubMed
-
- Alberola-Ila, J., K. A. Forbush, R. Seger, E. G. Krebs, and R. M. Perlmutter. 1995. Selective requirement for MAP kinase activation in thymocyte differentiation. Nature 373:620-623. - PubMed
-
- Aubry, S., and J. Charron. 2000. N-Myc shares cellular functions with c-Myc. DNA Cell Biol. 19:353-364. - PubMed
-
- Bhunia, A. K., H. Han, A. Snowden, and S. Chatterjee. 1996. Lactosylceramide stimulates Ras-GTP loading, kinases (MEK, Raf), p44 mitogen-activated protein kinase, and c-fos expression in human aortic smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 271:10660-10666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
