ADP-ribosylation factor/COPI-dependent events at the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi interface are regulated by the guanine nucleotide exchange factor GBF1
- PMID: 12808027
- PMCID: PMC194875
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-11-0730
ADP-ribosylation factor/COPI-dependent events at the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi interface are regulated by the guanine nucleotide exchange factor GBF1
Abstract
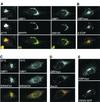
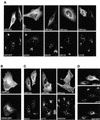
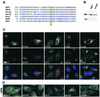
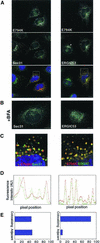
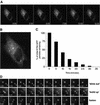
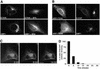
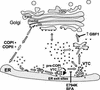
ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) mediated recruitment of COPI to membranes plays a central role in transport between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the Golgi. The activation of ARFs is mediated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs). Although several ARF-GEFs have been identified, the transport steps in which they function are still poorly understood. Here we report that GBF1, a member of the Sec7-domain family of GEFs, is responsible for the regulation of COPI-mediated events at the ER-Golgi interface. We show that GBF1 is essential for the formation, differentiation, and translocation of pre-Golgi intermediates and for the maintenance of Golgi integrity. We also show that the formation of transport-competent ER-to-Golgi intermediates proceeds in two stages: first, a COPI-independent event leads to the formation of an unstable compartment, which is rapidly reabsorbed in the absence of GBF1 activity. Second, the association of GBF1 with this compartment allows COPI recruitment and leads to its maturation into transport intermediates. The recruitment of GBF1 to this compartment is specifically inhibited by brefeldin A. Our findings imply that the continuous recruitment of GBF1 to spatially differentiated membrane domains is required for sustained membrane remodeling that underlies membrane traffic and Golgi biogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dissecting the role of the ARF guanine nucleotide exchange factor GBF1 in Golgi biogenesis and protein trafficking.J Cell Sci. 2007 Nov 15;120(Pt 22):3929-40. doi: 10.1242/jcs.010769. Epub 2007 Oct 23. J Cell Sci. 2007. PMID: 17956946
-
GBF1, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for ADP-ribosylation factors, is localized to the cis-Golgi and involved in membrane association of the COPI coat.Traffic. 2002 Jul;3(7):483-95. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2002.30705.x. Traffic. 2002. PMID: 12047556
-
Dissection of membrane dynamics of the ARF-guanine nucleotide exchange factor GBF1.Traffic. 2005 May;6(5):374-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00282.x. Traffic. 2005. PMID: 15813748
-
GBF1 and Arf1 function in vesicular trafficking, lipid homoeostasis and organelle dynamics.Biol Cell. 2017 Dec;109(12):391-399. doi: 10.1111/boc.201700042. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28985001 Review.
-
Regulating the large Sec7 ARF guanine nucleotide exchange factors: the when, where and how of activation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Sep;71(18):3419-38. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1602-7. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24728583 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kinetics of Arf1 inactivation regulates Golgi organisation and function in non-adherent fibroblasts.Biol Open. 2023 Apr 15;12(4):bio059669. doi: 10.1242/bio.059669. Epub 2023 May 4. Biol Open. 2023. PMID: 36946871 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of nicotinic receptor trafficking by the transmembrane Golgi protein UNC-50.EMBO J. 2007 Oct 17;26(20):4313-23. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601858. Epub 2007 Sep 13. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17853888 Free PMC article.
-
The ins and outs of the Arf4-based ciliary membrane-targeting complex.Small GTPases. 2021 Jan;12(1):1-12. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2019.1616355. Epub 2019 May 17. Small GTPases. 2021. PMID: 31068062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GTRAP3-18 serves as a negative regulator of Rab1 in protein transport and neuronal differentiation.J Cell Mol Med. 2009 Jan;13(1):114-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00303.x. Epub 2008 Mar 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 18363836 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of circular dorsal ruffles, macropinocytosis, and cell migration by RhoG and its exchange factor, Trio.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Jul 1;28(13):1768-1781. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-06-0412. Epub 2017 May 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28468978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achstetter, T., Franzusoff, A., Field, C., and Schekman, R. (1988). SEC7 encodes an unusual, high molecular weight protein required for membrane traffic from the yeast Golgi apparatus. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 11711-11717. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

