Citron kinase, a Rho-dependent kinase, induces di-phosphorylation of regulatory light chain of myosin II
- PMID: 12802051
- PMCID: PMC165073
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-07-0427
Citron kinase, a Rho-dependent kinase, induces di-phosphorylation of regulatory light chain of myosin II
Abstract
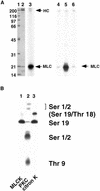
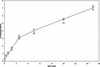
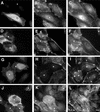
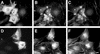
Citron kinase is a Rho-effector protein kinase that is related to Rho-associated kinases of ROCK/ROK/Rho-kinase family. Both ROCK and citron kinase are suggested to play a role in cytokinesis. However, no substrates are known for citron kinase. We found that citron kinase phosphorylated regulatory light chain (MLC) of myosin II at both Ser-19 and Thr-18 in vitro. Unlike ROCK, however, citron kinase did not phosphorylate the myosin binding subunit of myosin phosphatase, indicating that it does not inhibit myosin phosphatase. We found that the expression of the kinase domain of citron kinase resulted in an increase in MLC di-phosphorylation. Furthermore, the kinase domain was able to increase di-phosphorylation and restore stress fiber assembly even when ROCK was inhibited with a specific inhibitor, Y-27632. The expression of full-length citron kinase also increased di-phosphorylation during cytokinesis. These observations suggest that citron kinase phosphorylates MLC to generate di-phosphorylated MLC in vivo. Although both mono- and di-phosphorylated MLC were found in cleavage furrows, di-phosphorylated MLC showed more constrained localization than did mono-phosphorylated MLC. Because citron kinase is localized in cleavage furrows, citron kinase may be involved in regulating di-phosphorylation of MLC during cytokinesis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Thrombin-induced phosphorylation of the regulatory light chain of myosin II in cultured bovine corneal endothelial cells.Exp Eye Res. 2004 Oct;79(4):477-86. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2004.06.018. Exp Eye Res. 2004. PMID: 15381032
-
Phosphorylation of myosin-binding subunit (MBS) of myosin phosphatase by Rho-kinase in vivo.J Cell Biol. 1999 Nov 29;147(5):1023-38. doi: 10.1083/jcb.147.5.1023. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10579722 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct roles of ROCK (Rho-kinase) and MLCK in spatial regulation of MLC phosphorylation for assembly of stress fibers and focal adhesions in 3T3 fibroblasts.J Cell Biol. 2000 Aug 21;150(4):797-806. doi: 10.1083/jcb.150.4.797. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10953004 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of myosin II during cytokinesis in higher eukaryotes.Trends Cell Biol. 2005 Jul;15(7):371-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2005.05.004. Trends Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15935670 Review.
-
Role of myosin light chain phosphorylation in the regulation of cytokinesis.Cell Struct Funct. 2001 Dec;26(6):639-44. doi: 10.1247/csf.26.639. Cell Struct Funct. 2001. PMID: 11942620 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytokinesis failure in RhoA-deficient mouse erythroblasts involves actomyosin and midbody dysregulation and triggers p53 activation.Blood. 2015 Sep 17;126(12):1473-82. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-12-616169. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Blood. 2015. PMID: 26228485 Free PMC article.
-
Making the cut: the chemical biology of cytokinesis.ACS Chem Biol. 2010 Jan 15;5(1):79-90. doi: 10.1021/cb900256m. ACS Chem Biol. 2010. PMID: 20014865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drosophila citron kinase is required for the final steps of cytokinesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Nov;15(11):5053-63. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-06-0536. Epub 2004 Sep 15. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15371536 Free PMC article.
-
Anillin binds nonmuscle myosin II and regulates the contractile ring.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Jan;16(1):193-201. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-08-0758. Epub 2004 Oct 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15496454 Free PMC article.
-
A differentiation-dependent splice variant of myosin light chain kinase, MLCK1, regulates epithelial tight junction permeability.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 31;279(53):55506-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408822200. Epub 2004 Oct 26. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15507455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adelstein, R.S., and Klee, C.B. (1981a). Purification and characterization of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 256, 7501–7509. - PubMed
-
- Adelstein, R.S., and Klee, C.B. (1981b). Purification and characterization of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 256, 7501–7509. - PubMed
-
- Alessi, D., MacDougall, L.K., Sola, M.M., Ikebe, M., and Cohen, P. (1992). The control of protein phosphatase-1 by targetting subunits. The major myosin phosphatase in avian smooth muscle is a novel form of protein phosphatase-1. Eur. J. Biochem. 210, 1023–1035. - PubMed
-
- Amano, M., Chihara, K., Kimura, K., Fukata, Y., Nakamura, N., Matsuura, Y., and Kaibuchi, K. (1997). Formation of actin stress fibers and focal adhesions enhanced by Rho-kinase. Science 275, 1308–1311. - PubMed
-
- Amano, M., Ito, M., Kimura, K., Fukata, Y., Chihara, K., Nakano, T., Matsuura, Y., and Kaibuchi, K. (1996). Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase). J. Biol. Chem. 271, 20246–20249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

