Candida albicans VPS11 is required for vacuole biogenesis and germ tube formation
- PMID: 12796286
- PMCID: PMC161452
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.2.3.411-421.2003
Candida albicans VPS11 is required for vacuole biogenesis and germ tube formation
Abstract
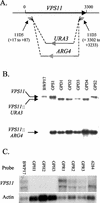
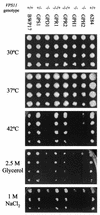
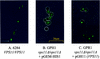
The Candida albicans vacuole has previously been observed to undergo rapid expansion during the emergence of a germ tube from a yeast cell, to occupy the majority of the parent yeast cell. Furthermore, the yeast-to-hypha switch has been implicated in the virulence of this organism. The class C vps (vacuolar protein sorting) mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are defective in multiple protein delivery pathways to the vacuole and prevacuole compartment. In this study C. albicans homologues of the S. cerevisiae class C VPS genes have been identified. Deletion of a C. albicans VPS11 homologue resulted in a number of phenotypes that closely resemble those of the class C vps mutants of S. cerevisiae, including the absence of a vacuolar compartment. The C. albicans vps11Delta mutant also had much-reduced secreted lipase and aspartyl protease activities. Furthermore, vps11Delta strains were defective in yeast-hypha morphogenesis. Upon serum induction of filamentous growth, mutants showed delayed emergence of germ tubes, had a reduced apical extension rate compared to those of control strains, and were unable to form mature hyphae. These results suggest that Vps11p-mediated trafficking steps are necessary to support the rapid emergence and extension of the germ tube from the parent yeast cell.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Candida albicans vacuole is required for differentiation and efficient macrophage killing.Eukaryot Cell. 2005 Oct;4(10):1677-86. doi: 10.1128/EC.4.10.1677-1686.2005. Eukaryot Cell. 2005. PMID: 16215175 Free PMC article.
-
Septin function in Candida albicans morphogenesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Aug;13(8):2732-46. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-01-0013. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12181342 Free PMC article.
-
Gpr1, a putative G-protein-coupled receptor, regulates morphogenesis and hypha formation in the pathogenic fungus Candida albicans.Eukaryot Cell. 2004 Aug;3(4):919-31. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.4.919-931.2004. Eukaryot Cell. 2004. PMID: 15302825 Free PMC article.
-
The distinct morphogenic states of Candida albicans.Trends Microbiol. 2004 Jul;12(7):317-24. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2004.05.008. Trends Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15223059 Review.
-
Glucose sensing network in Candida albicans: a sweet spot for fungal morphogenesis.Eukaryot Cell. 2009 Sep;8(9):1314-20. doi: 10.1128/EC.00138-09. Epub 2009 Jul 17. Eukaryot Cell. 2009. PMID: 19617394 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
A proteomic analysis of secretory proteins of a pre-vacuolar mutant of Candida albicans.J Proteomics. 2009 Dec 1;73(2):342-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2009.10.003. Epub 2009 Oct 9. J Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 19819358 Free PMC article.
-
HOPS-dependent endosomal fusion required for efficient cytosolic delivery of therapeutic peptides and small proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jan 8;116(2):512-521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1812044116. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30610181 Free PMC article.
-
Candida albicans VPS4 is required for secretion of aspartyl proteases and in vivo virulence.Mycopathologia. 2009 Feb;167(2):55-63. doi: 10.1007/s11046-008-9155-7. Epub 2008 Sep 24. Mycopathologia. 2009. PMID: 18814053 Free PMC article.
-
Vacuolar trafficking and Candida albicans pathogenesis.Commun Integr Biol. 2011 Mar;4(2):240-2. doi: 10.4161/cib.4.2.14717. Commun Integr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21655451 Free PMC article.
-
Trafficking through the late endosome significantly impacts Candida albicans tolerance of the azole antifungals.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Apr;59(4):2410-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04239-14. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25666149 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Arai, T., Y. Mikami, and K. Yokoyama. 1977. Phagocytosis of Candida albicans by rabbit alveolar macrophages and guinea pig neutrophils. Sabouraudia 15:171-177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

