Inflammatory breast cancer: relationship between growth factor signaling and motility in aggressive cancers
- PMID: 12793901
- PMCID: PMC165010
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr598
Inflammatory breast cancer: relationship between growth factor signaling and motility in aggressive cancers
Abstract
A variety of phenotypic characteristics are required for a cancer cell to successfully complete the metastatic cascade. Acquisition of a motile and invasive phenotype is one requirement for a cell to become metastatically competent. The Rho (Ras homology) GTPases are a subfamily of small GTP-binding proteins, which are related to the Ras oncogene. All aspects of cellular motility and invasion are controlled by the Rho GTPases and are closely linked to signals from the extracellular environment, particularly in response to growth factors. Dysregulation of Rho activation through aberrant growth-factor signaling, loss of function of key Rho-regulatory proteins or overexpression of Rho mRNA could result in increased Rho activity and cellular motility. Therefore, the importance of the Rho GTPases in the progression of aggressive cancers, is becoming more appreciated.
Figures
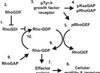
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of rho-associated kinase signaling prevents breast cancer metastasis to human bone.Cancer Res. 2009 Nov 15;69(22):8742-51. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1541. Epub 2009 Nov 3. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19887617
-
Rho GTPases: signaling, migration, and invasion.Exp Cell Res. 2000 Nov 25;261(1):1-12. doi: 10.1006/excr.2000.5049. Exp Cell Res. 2000. PMID: 11082269 Review.
-
Persistent activation of Rac1 in squamous carcinomas of the head and neck: evidence for an EGFR/Vav2 signaling axis involved in cell invasion.Carcinogenesis. 2007 Jun;28(6):1145-52. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgm008. Epub 2007 Jan 18. Carcinogenesis. 2007. PMID: 17234718
-
PRL tyrosine phosphatases regulate rho family GTPases to promote invasion and motility.Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 15;66(6):3153-61. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3116. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16540666
-
Altered Rho GTPase signaling pathways in breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004 Mar;84(1):43-8. doi: 10.1023/B:BREA.0000018422.02237.f9. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004. PMID: 14999153 Review.
Cited by
-
StarD13 is a tumor suppressor in breast cancer that regulates cell motility and invasion.Int J Oncol. 2014 May;44(5):1499-511. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2330. Epub 2014 Mar 7. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24627003 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappaB activation in inflammatory breast cancer is associated with oestrogen receptor downregulation, secondary to EGFR and/or ErbB2 overexpression and MAPK hyperactivation.Br J Cancer. 2007 Sep 3;97(5):659-69. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603906. Epub 2007 Aug 14. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17700572 Free PMC article.
-
Rac1 and Rac3 isoform activation is involved in the invasive and metastatic phenotype of human breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2005;7(6):R965-74. doi: 10.1186/bcr1329. Epub 2005 Sep 30. Breast Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16280046 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation profiling in Trisomy 21 females with and without breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 19;13:1203483. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1203483. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37538118 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion by RhoC GTPase and caveolin-1.Mol Cancer. 2005 Jun 21;4(1):21. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-4-21. Mol Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15969750 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Breast Cancer Facts and Figures 2001–2002. American Cancer Society, Atlanta, GA. 2002. http://www.cancer.org/downloads/STT/BrCaFF2001.pdf
-
- van Golen KL, Davies S, Wu ZF, Wang Y, Bucana CD, Root H, Chandrasekharappa S, Strawderman M, Ethier SP, Merajver SD. A novel putative low-affinity insulin-like growth factor-binding protein, LIBC (lost in inflammatory breast cancer), and RhoC GTPase correlate with the inflammatory breast cancer phenotype. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:2511–2519. - PubMed
-
- van Golen KL, Wu ZF, Qiao XT, Bao LW, Mearajver SD. RhoC GTPase, a novel transforming oncogene for human mammary epithelial cells that partially recapitulates the inflammatory breast cancer phenotype. Cancer Res. 2000;60:5832–5838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

