A lupus-like syndrome develops in mice lacking the Ro 60-kDa protein, a major lupus autoantigen
- PMID: 12788971
- PMCID: PMC164616
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0832411100
A lupus-like syndrome develops in mice lacking the Ro 60-kDa protein, a major lupus autoantigen
Abstract
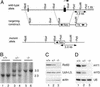
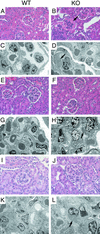
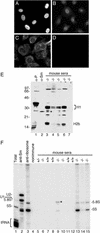
Antibodies against a conserved RNA-binding protein, the Ro 60-kDa autoantigen, occur in 24-60% of all patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Anti-Ro antibodies are correlated with photosensitivity and cutaneous lesions in these patients and with neonatal lupus, a syndrome in which mothers with anti-Ro antibodies give birth to children with complete congenital heart block and photosensitive skin lesions. In higher eukaryotes, the Ro protein binds small RNAs of unknown function known as Y RNAs. Because the Ro protein also binds misfolded 5S rRNA precursors, it is proposed to function in a quality-control pathway for ribosome biogenesis. Consistent with a role in the recognition or repair of intracellular damage, an orthologue of Ro in the radiation-resistant eubacterium Deinococcus radiodurans contributes to survival of this bacterium after UV irradiation. Here, we show that mice lacking the Ro protein develop an autoimmune syndrome characterized by anti-ribosome antibodies, anti-chromatin antibodies, and glomerulonephritis. Moreover, in one strain background, Ro-/- mice display increased sensitivity to irradiation with UV light. Thus, one function of this major human autoantigen may be to protect against autoantibody development, possibly by sequestering defective ribonucleoproteins from immune surveillance. Furthermore, the finding that mice lacking the Ro protein are photosensitive suggests that loss of Ro function could contribute to the photosensitivity associated with anti-Ro antibodies in humans.
Figures
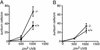
Similar articles
-
The Ro 60 kDa autoantigen: insights into cellular function and role in autoimmunity.J Mol Med (Berl). 2004 Apr;82(4):232-9. doi: 10.1007/s00109-004-0529-0. J Mol Med (Berl). 2004. PMID: 15168680 Review.
-
Ro ribonucleoproteins contribute to the resistance of Deinococcus radiodurans to ultraviolet irradiation.Genes Dev. 2000 Apr 1;14(7):777-82. Genes Dev. 2000. PMID: 10766734 Free PMC article.
-
The Ro autoantigen binds misfolded U2 small nuclear RNAs and assists mammalian cell survival after UV irradiation.Curr Biol. 2003 Dec 16;13(24):2206-11. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2003.11.028. Curr Biol. 2003. PMID: 14680639
-
Emerging roles for the Ro 60-kDa autoantigen in noncoding RNA metabolism.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Sep-Oct;2(5):686-99. doi: 10.1002/wrna.85. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21823229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptosis and redistribution of the Ro autoantigen in Balb/c mouse like in subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus.Clin Dev Immunol. 2006 Jun-Dec;13(2-4):163-6. doi: 10.1080/17402520600876796. Clin Dev Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17162359 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Broader Perspective on Anti-Ro Antibodies and Their Fetal Consequences-A Case Report and Literature Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Jul 14;10(7):478. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10070478. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32674462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retropseudogenes derived from the human Ro/SS-A autoantigen-associated hY RNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Apr 7;33(6):2032-41. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki504. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15817567 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of serum tripartite motif-containing 21 antibodies in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2006 May;97(5):380-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00192.x. Cancer Sci. 2006. PMID: 16630135 Free PMC article.
-
Functional requirement of noncoding Y RNAs for human chromosomal DNA replication.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Sep;26(18):6993-7004. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01060-06. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16943439 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular localisation and extracellular release of Y RNA and Y RNA binding proteins.J Extracell Biol. 2024 Jan 16;3(1):e123. doi: 10.1002/jex2.123. eCollection 2024 Jan. J Extracell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38938676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- von Muhlen, C. A. & Tan, E. M. (1995) Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 24, 323–358. - PubMed
-
- Provost, T. T., Watson, R. & Simmons-O'Brien, E. (1996) J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 35, 147–169. - PubMed
-
- Silverman, E. D. & Laxer, R. M. (1997) Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am. 23, 599–618. - PubMed
-
- Peek, R., Pruijn, G. J. M., van der Kemp, A. & van Venrooij, W. J. (1993) J. Cell Sci. 106, 929–935. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

