Towards an analysis of the rice mitochondrial proteome
- PMID: 12746528
- PMCID: PMC166968
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.102.018986
Towards an analysis of the rice mitochondrial proteome
Abstract
Purified rice (Oryza sativa) mitochondrial proteins have been arrayed by isoelectric focusing/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE), by blue-native (BN) PAGE, and by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (LC) separation (LC-mass spectrometry [MS]). From these protein arrays, we have identified a range of rice mitochondrial proteins, including hydrophilic/hydrophobic proteins (grand average of hydropathicity = -1.27 to +0.84), highly basic and acid proteins (isoelectric point = 4.0-12.5), and proteins over a large molecular mass range (6.7-252 kD), using proteomic approaches. BN PAGE provided a detailed picture of electron transport chain protein complexes. A total of 232 protein spots from isoelectric focusing/PAGE and BN PAGE separations were excised, trypsin digested, and analyzed by tandem MS (MS/MS). Using this dataset, 149 of the protein spots (the products of 91 nonredundant genes) were identified by searching translated rice open reading frames from genomic sequence and six-frame translated rice expressed sequence tags. Sequence comparison allowed us to assign functions to a subset of 85 proteins, including many of the major function categories expected for this organelle. A further six spots were matched to rice sequences for which no specific function has yet been determined. Complete digestion of mitochondrial proteins with trypsin yielded a peptide mixture that was analyzed directly by reverse-phase LC via organic solvent elution from a C-18 column (LC-MS). These data yielded 170 MS/MS spectra that matched 72 sequence entries from open reading frame and expressed sequence tag databases. Forty-five of these were obtained using LC-MS alone, whereas 28 proteins were identified by both LC-MS and gel-based separations. In total, 136 nonredundant rice proteins were identified, including a new set of 23 proteins of unknown function located in plant mitochondria. We also report the first direct identification, to our knowledge, of PPR (pentatricopeptide repeat) proteins in the plant mitochondrial proteome. This dataset provides the first extensive picture, to our knowledge, of mitochondrial functions in a model monocot plant.
Figures

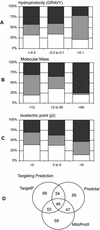
Similar articles
-
Experimental analysis of the rice mitochondrial proteome, its biogenesis, and heterogeneity.Plant Physiol. 2009 Feb;149(2):719-34. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.131300. Epub 2008 Nov 14. Plant Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19010998 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the mitochondrial proteome during the anoxia to air transition in rice focus around cytochrome-containing respiratory complexes.J Biol Chem. 2004 Sep 17;279(38):39471-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406015200. Epub 2004 Jul 16. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15258153
-
IEF peptide fractionation method combined to shotgun proteomics enhances the exploration of rice milk proteome.Anal Biochem. 2017 Nov 15;537:72-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2017.08.021. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Anal Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28864145
-
Systems Biochemistry Approaches to Defining Mitochondrial Protein Function.Cell Metab. 2020 Apr 7;31(4):669-678. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.03.011. Cell Metab. 2020. PMID: 32268114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteome analysis: genomics via the output rather than the input code.J Protein Chem. 1997 Jul;16(5):537-44. doi: 10.1023/a:1026330015280. J Protein Chem. 1997. PMID: 9246641 Review.
Cited by
-
The rice mitochondria proteome and its response during development and to the environment.Front Plant Sci. 2013 Feb 7;4:16. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00016. eCollection 2013. Front Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 23403394 Free PMC article.
-
Supramolecular organization of the respiratory chain in Neurospora crassa mitochondria.Eukaryot Cell. 2007 Dec;6(12):2391-405. doi: 10.1128/EC.00149-07. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Eukaryot Cell. 2007. PMID: 17873079 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the respiratory chain of plant mitochondria. Supercomplexes and a unique composition of complex II.Plant Physiol. 2003 Sep;133(1):274-86. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.024620. Plant Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12970493 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen peroxide acts on sensitive mitochondrial proteins to induce death of a fungal pathogen revealed by proteomic analysis.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21945. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021945. Epub 2011 Jul 6. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21755012 Free PMC article.
-
Ordered assembly of mitochondria during rice germination begins with pro-mitochondrial structures rich in components of the protein import apparatus.Plant Mol Biol. 2006 Jan;60(2):201-23. doi: 10.1007/s11103-005-3688-7. Plant Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16429260
References
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 2000;408:796–815. - PubMed
-
- Bardel J, Louwagie M, Jaquinod M, Jourdain A, Luche S, Rabilloud T, Macherel D, Garin J, Bourguignon J. A survey of the plant mitochondrial proteome in relation to development. Proteomics. 2002;2:880–898. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

