Polo-like kinase (Plk)1 depletion induces apoptosis in cancer cells
- PMID: 12732729
- PMCID: PMC156279
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1031523100
Polo-like kinase (Plk)1 depletion induces apoptosis in cancer cells
Abstract
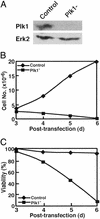
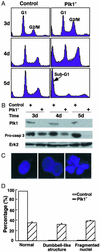
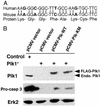
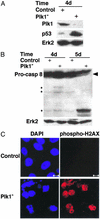
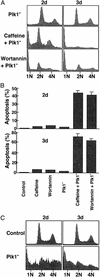
Elevated expression of mammalian polo-like kinase (Plk)1 occurs in many different types of cancers, and Plk1 has been proposed as a novel diagnostic marker for several tumors. We used the recently developed vector-based small interfering RNA technique to specifically deplete Plk1 in cancer cells. We found that Plk1 depletion dramatically inhibited cell proliferation, decreased viability, and resulted in cell-cycle arrest with 4 N DNA content. The formation of dumbbell-like chromatin structure suggests the inability of these cells to completely separate the sister chromatids at the onset of anaphase. Plk1 depletion induced apoptosis, as indicated by the appearance of subgenomic DNA in fluorescence-activated cell-sorter (FACS) profiles, the activation of caspase 3, and the formation of fragmented nuclei. Plk1-depletion-induced apoptosis was partially reversed by cotransfection of nondegradable mouse Plk1 constructs. In addition, the p53 pathway was shown to be involved in Plk1-depletion-induced apoptosis. DNA damage occurred in Plk1-depleted cells and inhibition of ATM strongly potentiated the lethality of Plk1 depletion. Although p53 is stabilized in Plk1-depleted cells, DNA damage also occurs in p53(-/-) cells. These data support the notion that disruption of Plk1 function could be an important application in cancer therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Small interfering RNA-mediated Polo-like kinase 1 depletion preferentially reduces the survival of p53-defective, oncogenic transformed cells and inhibits tumor growth in animals.Cancer Res. 2005 Apr 1;65(7):2698-704. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2131. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15805268
-
Normal cells, but not cancer cells, survive severe Plk1 depletion.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Mar;26(6):2093-108. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.6.2093-2108.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16507989 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Cdc2/cyclin B and inhibition of centrosome amplification in cells depleted of Plk1 by siRNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Jun 25;99(13):8672-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.132269599. Epub 2002 Jun 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12077309 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of antisense RNA targeting polo-like kinase 1 on cell cycle and proliferation in A549 cells.Chin Med J (Engl). 2004 Nov;117(11):1642-9. Chin Med J (Engl). 2004. PMID: 15569479
-
Differential regulation of polo-like kinase 1, 2, 3, and 4 gene expression in mammalian cells and tissues.Oncogene. 2005 Jan 10;24(2):260-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208219. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15640841 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of the polo-like kinase inhibitor rigosertib, alone or in combination with Abelson tyrosine kinase inhibitors, against break point cluster region-c-Abelson-positive leukemia cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 21;6(24):20231-40. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4047. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26008977 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of adavosertib therapy against anaplastic thyroid cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2021 Apr 29;28(5):311-324. doi: 10.1530/ERC-21-0001. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33769310 Free PMC article.
-
Increases in mitochondrial DNA content and 4977-bp deletion upon ATM/Chk2 checkpoint activation in HeLa cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40572. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040572. Epub 2012 Jul 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22808196 Free PMC article.
-
G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 modifies cancer cell resistance to paclitaxel.Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 Nov;461(1-2):103-118. doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03594-9. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31363957
-
α-Santalol functionalized chitosan nanoparticles as efficient inhibitors of polo-like kinase in triple negative breast cancer.RSC Adv. 2020 Feb 3;10(9):5487-5501. doi: 10.1039/c9ra09084c. eCollection 2020 Jan 29. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35498298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glover D M, Hagan I M, Tavares A A M. Genes Dev. 1998;12:3777–3787. - PubMed
-
- Nigg E A. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1998;10:776–783. - PubMed
-
- Strebhardt K. In: PLK (Polo-Like Kinase): Encyclopedia of Molecular Medicine. Creighton T E, editor. New York: Wiley; 2001. pp. 2530–2532.
-
- Knecht R, Elez R, Oechler M, Solbach C, von Ilberg C, Strebhardt K. Cancer Res. 1999;59:2794–2797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

