Phylogenetic analysis of anaerobic psychrophilic enrichment cultures obtained from a greenland glacier ice core
- PMID: 12676695
- PMCID: PMC154775
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.69.4.2153-2160.2003
Phylogenetic analysis of anaerobic psychrophilic enrichment cultures obtained from a greenland glacier ice core
Abstract
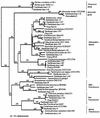
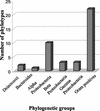
The examination of microorganisms in glacial ice cores allows the phylogenetic relationships of organisms frozen for thousands of years to be compared with those of current isolates. We developed a method for aseptically sampling a sediment-containing portion of a Greenland ice core that had remained at -9 degrees C for over 100,000 years. Epifluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry results showed that the ice sample contained over 6 x 10(7) cells/ml. Anaerobic enrichment cultures inoculated with melted ice were grown and maintained at -2 degrees C. Genomic DNA extracted from these enrichments was used for the PCR amplification of 16S rRNA genes with bacterial and archaeal primers and the preparation of clone libraries. Approximately 60 bacterial inserts were screened by restriction endonuclease analysis and grouped into 27 unique restriction fragment length polymorphism types, and 24 representative sequences were compared phylogenetically. Diverse sequences representing major phylogenetic groups including alpha, beta, and gamma Proteobacteria as well as relatives of the Thermus, Bacteroides, Eubacterium, and Clostridium groups were found. Sixteen clone sequences were closely related to those from known organisms, with four possibly representing new species. Seven sequences may reflect new genera and were most closely related to sequences obtained only by PCR amplification. One sequence was over 12% distant from its closest relative and may represent a novel order or family. These results show that phylogenetically diverse microorganisms have remained viable within the Greenland ice core for at least 100,000 years.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phylogenetic and physiological diversity of microorganisms isolated from a deep greenland glacier ice core.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 Jan;70(1):202-13. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.1.202-213.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 14711643 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and isolation of ultrasmall microorganisms from a 120,000-year-old Greenland glacier ice core.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Dec;71(12):7806-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.12.7806-7818.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16332755 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial diversity in Malan ice core from the Tibetan Plateau.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2004;49(3):269-75. doi: 10.1007/BF02931042. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2004. PMID: 15259767
-
Comparison of the microbial diversity at different depths of the GISP2 Greenland ice core in relationship to deposition climates.Environ Microbiol. 2009 Mar;11(3):640-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01835.x. Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19278450
-
Isolation and phylogenetic classification of culturable psychrophilic prokaryotes from the Collins glacier in the Antarctica.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2011 May;56(3):209-14. doi: 10.1007/s12223-011-0038-9. Epub 2011 May 31. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2011. PMID: 21625878
Cited by
-
Cultivable bacteria in the supraglacial lake formed after a glacial lake outburst flood in northern Pakistan.Int Microbiol. 2023 May;26(2):309-325. doi: 10.1007/s10123-022-00306-0. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Int Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36484912
-
Microbial community succession in an unvegetated, recently deglaciated soil.Microb Ecol. 2007 Jan;53(1):110-22. doi: 10.1007/s00248-006-9144-7. Epub 2006 Dec 22. Microb Ecol. 2007. PMID: 17186150
-
Contamination analysis of Arctic ice samples as planetary field analogs and implications for future life-detection missions to Europa and Enceladus.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 27;12(1):12379. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16370-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35896693 Free PMC article.
-
A Submersible, Off-Axis Holographic Microscope for Detection of Microbial Motility and Morphology in Aqueous and Icy Environments.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 26;11(1):e0147700. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147700. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26812683 Free PMC article.
-
Culturable bacteria in glacial meltwater at 6,350 m on the East Rongbuk Glacier, Mount Everest.Extremophiles. 2009 Jan;13(1):89-99. doi: 10.1007/s00792-008-0200-8. Epub 2008 Nov 18. Extremophiles. 2009. PMID: 19015814
References
-
- Baross, J. A., and R. Y. Morita. 1978. Microbial life at low temperatures: ecological aspects, p. 9-71. In J. Kushner (ed.), Microbial life in extreme environments. Academic Press, New York, N.Y.
-
- Brambilla, E., H. Hippe, A. Hagelstein, G. Tindall, and E. Stackebrandt. 2001. 16S rDNA diversity of cultured and uncultured prokaryotes of a mat sample from Lake Fryxell, McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Extremophiles 5:23-33. - PubMed
-
- Brenchley, J. E. 1996. Psychrophilic microorganisms and their cold-active enzymes. J. Ind. Microbiol. 17:432-437.
-
- Cato, E. P., W. L. George, and S. M. Finegold. 1986. Genus Clostridium Prazmowski 1880, 23AL, p. 1141-1200. In P. H. A. Sneath, N. S. Mair, M. E. Sharpe, and J. G. Holt (ed.), Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology, vol. 2. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, Md.
-
- Christner, B. C., E. Mosley-Thompson, L. G. Thompson, and J. N. Reeve. 2001. Isolation of bacteria and 16S rDNAs from Lake Vostok accretion ice. Environ. Microbiol. 3:570-577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

