Human Sin3 deacetylase and trithorax-related Set1/Ash2 histone H3-K4 methyltransferase are tethered together selectively by the cell-proliferation factor HCF-1
- PMID: 12670868
- PMCID: PMC196026
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.252103
Human Sin3 deacetylase and trithorax-related Set1/Ash2 histone H3-K4 methyltransferase are tethered together selectively by the cell-proliferation factor HCF-1
Abstract
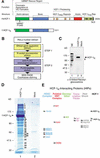
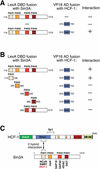
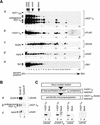
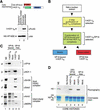
The abundant and chromatin-associated protein HCF-1 is a critical player in mammalian cell proliferation as well as herpes simplex virus (HSV) transcription. We show here that separate regions of HCF-1 critical for its role in cell proliferation associate with the Sin3 histone deacetylase (HDAC) and a previously uncharacterized human trithorax-related Set1/Ash2 histone methyltransferase (HMT). The Set1/Ash2 HMT methylates histone H3 at Lys 4 (K4), but not if the neighboring K9 residue is already methylated. HCF-1 tethers the Sin3 and Set1/Ash2 transcriptional regulatory complexes together even though they are generally associated with opposite transcriptional outcomes: repression and activation of transcription, respectively. Nevertheless, this tethering is context-dependent because the transcriptional activator VP16 selectively binds HCF-1 associated with the Set1/Ash2 HMT complex in the absence of the Sin3 HDAC complex. These results suggest that HCF-1 can broadly regulate transcription, both positively and negatively, through selective modulation of chromatin structure.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Evidence that Set1, a factor required for methylation of histone H3, regulates rDNA silencing in S. cerevisiae by a Sir2-independent mechanism.Curr Biol. 2002 Jan 22;12(2):165-70. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(01)00652-2. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 11818070
-
E2F activation of S phase promoters via association with HCF-1 and the MLL family of histone H3K4 methyltransferases.Mol Cell. 2007 Jul 6;27(1):107-19. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.05.030. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17612494
-
Leukemia proto-oncoprotein MLL forms a SET1-like histone methyltransferase complex with menin to regulate Hox gene expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Jul;24(13):5639-49. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.13.5639-5649.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15199122 Free PMC article.
-
Co-repressor, co-activator and general transcription factor: the many faces of the Sin3 histone deacetylase (HDAC) complex.Biochem J. 2018 Dec 14;475(24):3921-3932. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170314. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 30552170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The herpes simplex virus VP16-induced complex: the makings of a regulatory switch.Trends Biochem Sci. 2003 Jun;28(6):294-304. doi: 10.1016/S0968-0004(03)00088-4. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003. PMID: 12826401 Review.
Cited by
-
A combination of H2A.Z and H4 acetylation recruits Brd2 to chromatin during transcriptional activation.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(11):e1003047. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003047. Epub 2012 Nov 8. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23144632 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamics of HCF-1 modulation of herpes simplex virus chromatin during initiation of infection.Viruses. 2013 May 22;5(5):1272-91. doi: 10.3390/v5051272. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23698399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pluripotency maintenance mechanism of embryonic stem cells and reprogramming.Int J Hematol. 2010 Apr;91(3):360-72. doi: 10.1007/s12185-010-0517-9. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Int J Hematol. 2010. PMID: 20157790 Review.
-
Members of the H3K4 trimethylation complex regulate lifespan in a germline-dependent manner in C. elegans.Nature. 2010 Jul 15;466(7304):383-7. doi: 10.1038/nature09195. Epub 2010 Jun 16. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20555324 Free PMC article.
-
Physical and functional interaction between SET1/COMPASS complex component CFP-1 and a Sin3S HDAC complex in C. elegans.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Dec 2;47(21):11164-11180. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz880. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31602465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bryk M, Briggs SD, Strahl BD, Curcio MJ, Allis CD, Winston F. Evidence that Set1, a factor required for methylation of histone H3, regulates rDNA silencing in S. cerevisiae by a Sir2-independent mechanism. Curr Biol. 2002;12:165–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
