Adjuvant-dependent modulation of Th1 and Th2 responses to immunization with beta-amyloid
- PMID: 12663680
- PMCID: PMC1483061
- DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxg049
Adjuvant-dependent modulation of Th1 and Th2 responses to immunization with beta-amyloid
Abstract
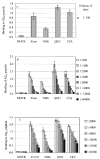
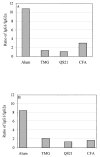
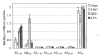
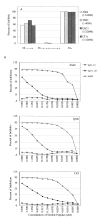
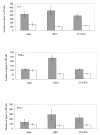
The role of adjuvant on the T(h)1 and T(h)2 immune responses to Abeta-immunotherapy (Abeta(42 )peptide) was examined in wild-type mice. Fine epitope analysis with overlapping oligomers of the Abeta(42) sequence identified the 1-15 region as a dominant B cell epitope. The 6-20 peptide was recognized only weakly by antisera from mice administrated with Abeta(42) peptide formulated in complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA), alum or TiterMax Gold (TMG). However, mice immunized with Abeta(42) mixed with QS21 induced a significant antibody response to the 6-20 peptide. The only T cell epitope found was within the 6-28 sequence of Abeta(42). QS21 and CFA induced the strongest humoral response to Abeta, alum was intermediate, and TMG the weakest adjuvant. Analysis of antibody isotypes specific for Abeta indicates that alum induces primarily T(h)2-type immune response, whereas TMG, CFA and QS21 shift the immune responses toward a T(h)1 phenotype. Stimulation of splenocytes from Abeta-immunized mice with Abeta(40) peptide induced strikingly different cytokine expression profiles. QS21 and CFA induced significant IFN-gamma, IL-4 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression, whereas alum induced primarily IL-4 production. As T(h)1-type immune responses have been implicated in many autoimmune disorders, whereas T(h)2-type responses have been shown to inhibit autoimmune disease, the choice of adjuvant may be critical for the design of a safe and effective immunotherapy for Alzheimer's disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prototype Alzheimer's disease epitope vaccine induced strong Th2-type anti-Abeta antibody response with Alum to Quil A adjuvant switch.Vaccine. 2006 Mar 20;24(13):2275-82. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2005.11.039. Epub 2005 Dec 5. Vaccine. 2006. PMID: 16368167 Free PMC article.
-
Prototype Alzheimer's disease vaccine using the immunodominant B cell epitope from beta-amyloid and promiscuous T cell epitope pan HLA DR-binding peptide.J Immunol. 2005 Feb 1;174(3):1580-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.3.1580. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15661919
-
In interleukin-4-deficient mice, alum not only generates T helper 1 responses equivalent to freund's complete adjuvant, but continues to induce T helper 2 cytokine production.Eur J Immunol. 1996 Sep;26(9):2062-6. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260915. Eur J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8814247
-
Reduced Th1 and enhanced Th2 immunity after immunization with Alzheimer's beta-amyloid(1-42).J Neuroimmunol. 2002 Nov;132(1-2):49-59. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(02)00307-7. J Neuroimmunol. 2002. PMID: 12417433
-
Deviation of the allergic IgE to an IgG response by gene immunotherapy.Int Rev Immunol. 1999;18(3):271-89. doi: 10.3109/08830189909043030. Int Rev Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10614729 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunotherapeutic efficiency of a tetravalent Aβ1-15 vaccine in APP/PS1 transgenic mice as mouse model for Alzheimer's disease.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013 Aug;9(8):1643-53. doi: 10.4161/hv.24830. Epub 2013 May 31. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23732905 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Borrelia burgdorferi BbHtrA Protease as a Vaccine Candidate for Lyme Borreliosis in Mice.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 15;10(6):e0128868. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128868. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26076465 Free PMC article.
-
Mannan-Abeta28 conjugate prevents Abeta-plaque deposition, but increases microhemorrhages in the brains of vaccinated Tg2576 (APPsw) mice.J Neuroinflammation. 2008 Sep 29;5:42. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-5-42. J Neuroinflammation. 2008. PMID: 18823564 Free PMC article.
-
MultiTEP platform-based DNA vaccines for alpha-synucleinopathies: preclinical evaluation of immunogenicity and therapeutic potency.Neurobiol Aging. 2017 Nov;59:156-170. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.08.006. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Neurobiol Aging. 2017. PMID: 28870518 Free PMC article.
-
Phytol-derived novel isoprenoid immunostimulants.Front Immunol. 2012 Mar 22;3:49. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00049. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22566931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Price DL, Sisodia SS. Cellular and molecular biology of Alzheimer’s disease and animal models. Annu Rev Med. 1994;45:435. - PubMed
-
- Verbeek MM, de Waal RM, Schipper JJ, Van Nostrand WE. Rapid degeneration of cultured human brain pericytes by amyloid beta protein. J Neurochem. 1997;68:1135. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:741. - PubMed
-
- Helmuth L. New Alzheimer’s treatment that may ease the mind. Science. 2002;297:1260. - PubMed
-
- Schenk D, Barbour R, Dunn W, Gordon G, Grajeda H, Guido T, Hu K, Huang J, Johnson-Wood K, Khan K, Kholodenko D, Lee M, Liao Z, Lieberburg I, Motter R, Mutter L, Soriano F, Shopp G, Vasquez N, Vandevert C, Walker S, Wogulis M, Yednock T, Games D, Seubert P. Immunization with amyloid-beta attenuates Alzheimer-disease-like pathology in the PDAPP mouse [see Comments] Nature. 1999;400:173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

