Reversal of Taxol resistance in hepatoma by cyclosporin A: involvement of the PI-3 kinase-AKT 1 pathway
- PMID: 12644839
- PMCID: PMC2377082
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600788
Reversal of Taxol resistance in hepatoma by cyclosporin A: involvement of the PI-3 kinase-AKT 1 pathway
Abstract
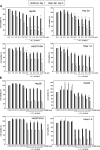
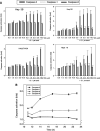
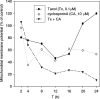
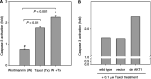
Hepatoma cells are known to be highly resistant to chemotherapy. Previously, we have found differential Taxol resistance in human and murine hepatoma cells. The aim of this study was to examine the effect of a multidrug resistance inhibitor, cyclosporin A in combination with Taxol on hepatoma in vitro and in vivo, and to identify the possible mechanism involved in Taxol resistance. Simultaneous treatment of cyclosporin A (0-10 microM) and Taxol (0.1 microM) inhibited cell growth in vitro. Cyclosporin A interfered with Taxol (0.1 microM)-induced AKT activation and BAD phosphorylation. Cyclosporin A combined with Taxol treatment augments caspase-9, -3 activation and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential in HepG2 cells. PI3 kinase inhibitor, wortmannin, or a dominant-negative AKT1 expression vector treatment partially enhanced Taxol-induced apoptosis indicating that PI3 kinase-AKT pathway was involved in Taxol-resistance pathway. Moreover, combination treatment reduced tumour growth in SCID and C57BL/6 mice as compared to either Taxol or cyclosporin A treatment. Our results indicate that the combination of cyclosporin A and Taxol is effective in the reversal of Taxol resistance through the inhibition of PI3 kinase-AKT1 pathway.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inactivation of the antiapoptotic phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway by the combined treatment of taxol and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibition.Clin Cancer Res. 2002 Jul;8(7):2091-9. Clin Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12114408
-
[Reversal effect of PI-3K/Akt pathway inhibitor LY294002 on multidrug resistance of ovarian cancer cell line A2780/Taxol].Ai Zheng. 2008 Apr;27(4):343-7. Ai Zheng. 2008. PMID: 18423117 Chinese.
-
PARP-1 inhibition-induced activation of PI-3-kinase-Akt pathway promotes resistance to taxol.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Apr 15;77(8):1348-57. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.01.008. Epub 2009 Jan 24. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19426673
-
FTY720 induces apoptosis of human hepatoma cell lines through PI3-K-mediated Akt dephosphorylation.Carcinogenesis. 2004 Dec;25(12):2397-405. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgh250. Epub 2004 Aug 5. Carcinogenesis. 2004. PMID: 15297371
-
Inhibition of phosphorylation of BAD and Raf-1 by Akt sensitizes human ovarian cancer cells to paclitaxel.J Biol Chem. 2002 Sep 6;277(36):33490-500. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M204042200. Epub 2002 Jun 26. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12087097
Cited by
-
Demethylation of HIN-1 reverses paclitaxel-resistance of ovarian clear cell carcinoma through the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway.BMC Cancer. 2015 Oct 24;15:789. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1744-5. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26497956 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatoma BEL-7402 cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Sep;9(9):1968-71. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i9.1968. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12970886 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Conventional Synthetic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs with Antineoplastic Potential: a Review.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022 Apr;12(4):835-860. doi: 10.1007/s13555-022-00713-1. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022. PMID: 35381976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of genes associated with SiHa cell sensitivity to paclitaxel by CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screening.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Apr 1;11(4):1972-1978. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31938303 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating constitutive gene expression and chemoactivity: mining the NCI60 anticancer screen.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e44631. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044631. Epub 2012 Oct 2. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23056181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bowers DC, Fan S, Walter KA, Abounader R, Williams JA, Rosen EM, Laterra J (2000) Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor protects against cytotoxic death in human glioblastoma via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase- and AKT-dependent pathways. Cancer Res 60: 4277–4283 - PubMed
-
- Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, Frisch S (1998) Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science 282: 1318–1321 - PubMed
-
- Cavalieri EL, Stack DE, Devanesan PD, Todorovic R, Dwivedy I, Higginbotham S, Johansson SL, Patil KD, Gross ML, Gooden JK, Ramanathan R, Cerny RL, Rogan EG (1997) Molecular origin of cancer: catechol estrogen-3,4-quinones as endogenous tumour initiators. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 10937–10942 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chabner BA (1991) Taxol. Princ Pract Oncol 5: 1–10
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

