Nuclear and cytosolic calcium are regulated independently
- PMID: 12606721
- PMCID: PMC151451
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0536590100
Nuclear and cytosolic calcium are regulated independently
Abstract
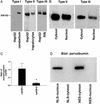
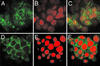
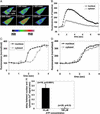
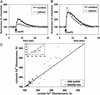
Nuclear calcium (Ca(2+)) regulates a number of important cellular processes, including gene transcription, growth, and apoptosis. However, it is unclear whether Ca(2+) signaling is regulated differently in the nucleus and cytosol. To investigate this possibility, we examined subcellular mechanisms of Ca(2+) release in the HepG2 liver cell line. The type II isoform of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP(3)) receptor (InsP(3)R) was expressed to a similar extent in the endoplasmic reticulum and nucleus, whereas the type III InsP(3)R was concentrated in the endoplasmic reticulum, and the type I isoform was not expressed. Ca(2+) signals induced by low InsP(3) concentrations started earlier or were larger in the nucleus than in the cytosol, indicating higher sensitivity of nuclear Ca(2+) stores for InsP(3). Nuclear InsP(3)R channels were active at lower InsP(3) concentrations than InsP(3)R from cytosol. Enriched expression of type II InsP(3)R in the nucleus results in greater sensitivity of the nucleus to InsP(3), thus providing a mechanism for independent regulation of Ca(2+)-dependent processes in this cellular compartment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of Ca(2+) signaling in rat bile duct epithelia by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor isoforms.Hepatology. 2002 Aug;36(2):284-96. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.34432. Hepatology. 2002. PMID: 12143036 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the type III InsP(3) receptor by InsP(3) and calcium.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002 Jun 14;294(3):719-25. doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00524-7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002. PMID: 12056830
-
Type 3 inositol trisphosphate receptors in RINm5F cells are biphasically regulated by cytosolic Ca2+ and mediate quantal Ca2+ mobilization.Biochem J. 1999 Nov 15;344 Pt 1(Pt 1):55-60. Biochem J. 1999. PMID: 10548533 Free PMC article.
-
Bi-directional signalling from the InsP3 receptor: regulation by calcium and accessory factors.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Oct;31(Pt 5):950-3. doi: 10.1042/bst0310950. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 14505456 Review.
-
Redoxing calcium from the ER.Cell. 2005 Jan 14;120(1):4-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.034. Cell. 2005. PMID: 15652474 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential subcellular Ca2+ signaling in a highly specialized subpopulation of astrocytes.Exp Neurol. 2015 Mar;265:59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.12.014. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Exp Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25542978 Free PMC article.
-
Junctional membrane inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor complex coordinates sensitization of the silent EGF-induced Ca2+ signaling.J Cell Biol. 2005 May 23;169(4):657-67. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200411034. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15911880 Free PMC article.
-
Hormonal regulation of nuclear permeability.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 9;282(6):4210-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M606300200. Epub 2006 Dec 7. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17158097 Free PMC article.
-
IP3-dependent nuclear Ca2+ signalling in the mammalian heart.J Physiol. 2007 Oct 15;584(Pt 2):601-11. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.140731. Epub 2007 Aug 30. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17761776 Free PMC article.
-
Central and Peripheral Nervous System Progenitors Derived from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Reveal a Unique Temporal and Cell-Type Specific Expression of PMCAs.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018 Feb 6;6:5. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00005. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29468158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clapham D E. Cell. 1995;80:259–268. - PubMed
-
- Berridge M J, Lipp P, Bootman M D. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000;1:11–21. - PubMed
-
- Carrion A M, Link W A, Ledo F, Mellstrom B, Naranjo J R. Nature. 1999;398:80–84. - PubMed
-
- Chawla S, Hardingham G E, Quinn D R, Bading H. Science. 1998;281:1505–1509. - PubMed
-
- Hardingham G E, Chawla S, Johnson C M, Bading H. Nature. 1997;385:260–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

