6. Asthma
- PMID: 12592297
- PMCID: PMC7112293
- DOI: 10.1067/mai.2003.94
6. Asthma
Abstract
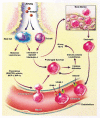
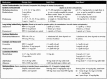
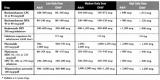
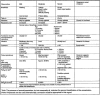
The increasing incidence and prevalence of asthma in many parts of the world continue to make it a global health concern. The heterogeneous nature of the clinical manifestations and therapeutic responses of asthma in both adult and pediatric patients indicate that it may be more of a syndrome rather than a specific disease entity. Numerous triggering factors including viral infections, allergen and irritant exposure, and exercise, among others, complicate both the acute and chronic treatment of asthma. Therapeutic intervention has focused on the appreciation that airway obstruction in asthma is composed of both bronchial smooth muscle spasm and variable degrees of airway inflammation characterized by edema, mucus secretion, and the influx of a variety of inflammatory cells. The presence of only partial reversibility of airflow obstruction in some patients indicates that structural remodeling of the airways may also occur over time. Choosing appropriate medications depends on the disease severity (intermittent, mild persistent, moderate persistent, severe persistent), extent of reversibility, both acutely and chronically, patterns of disease activity (exacerbations related to viruses, allergens, exercise, etc), and the age of onset (infancy, childhood, adulthood).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Asthma.JAMA. 1997 Dec 10;278(22):1855-73. JAMA. 1997. PMID: 9396647 Review.
-
Understanding asthma pathophysiology.Allergy Asthma Proc. 2003 Mar-Apr;24(2):79-83. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2003. PMID: 12776439 Review.
-
[Allergic inflammation in the development of nonspecific bronchial hyperresponsiveness in asthma].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2002 Jun;12(72):515-8. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2002. PMID: 12362673 Review. Polish.
-
Evaluation of severity of bronchial asthma through an exercise bronchial challenge.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2005 Nov;40(5):457-63. doi: 10.1002/ppul.20275. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2005. PMID: 16175592 Clinical Trial.
-
Provoked models of asthma: what have we learnt?Clin Exp Allergy. 2009 Feb;39(2):181-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.03172.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009. PMID: 19187330 Review.
Cited by
-
CD4⁺ and CD8⁺ T cells play a central role in a HDM driven model of allergic asthma.Respir Res. 2016 Apr 25;17:45. doi: 10.1186/s12931-016-0359-y. Respir Res. 2016. PMID: 27112462 Free PMC article.
-
Non-genomic Effects of Glucocorticoids: An Updated View.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Jan;40(1):38-49. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.11.002. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30497693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Rhino-Sinusitis and Asthma: Concept of Unified Airway Disease (UAD) and its Impact in Otolaryngology.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013 Aug;65(Suppl 2):338-42. doi: 10.1007/s12070-012-0495-8. Epub 2012 Feb 2. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013. PMID: 24427673 Free PMC article.
-
Allergic Asthma-Induced Cognitive Impairment is Alleviated by Dexamethasone.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 23;12:680815. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.680815. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34248632 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of a murine model of the late asthmatic response.Respir Res. 2017 Apr 11;18(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12931-017-0541-x. Respir Res. 2017. PMID: 28399855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cookson WO. Asthma genetics. Chest. 2002;121(3 Suppl):7S–13S. - PubMed
-
- Van Eerdewegh P, Little RD, Dupuis J, Del Mastro RG, Falls K, Simon J. Association of the ADAM33 gene with asthma and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Nature. 2002;418:426–430. - PubMed
-
- Israel E, Drazen JM, Liggett SB, Boushey HA, Cherniack RM, Chinchilli VM. The effect of polymorphisms of the b2-adrenergic receptor on the response to regular use of albuterol in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;162:75–80. - PubMed
-
- Palmer LJ, Silverman ES, Weiss ST, Drazen JM. Pharmacogenetics of asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:861–866. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

