Epidemic hand, foot and mouth disease caused by human enterovirus 71, Singapore
- PMID: 12533285
- PMCID: PMC2873753
- DOI: 10.3201/eid0901.020112
Epidemic hand, foot and mouth disease caused by human enterovirus 71, Singapore
Abstract
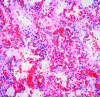
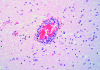
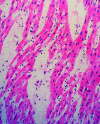
Singapore experienced a large epidemic of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) in 2000. After reviewing HFMD notifications from doctors and child-care centers, we found that the incidence of HFMD rose in September and declined at the end of October. During this period, 3,790 cases were reported. We performed enteroviral cultures on 311 and 157 specimens from 175 HFMD patients and 107 non-HFMD patients, respectively; human enterovirus 71 (HEV71) was the most frequently isolated virus from both groups. Most of the HFMD patients were </=4 years of age. Three HFMD and two non-HFMD patients died. Specimens from two HFMD and both non-HFMD patients were culture positive for HEV71; a third patient was possibly associated with the virus. Autopsies performed on all three HFMD and one of the non-HFMD case-patients showed encephalitis, interstitial pneumonitis, and myocarditis. A preparedness plan for severe HFMD outbreaks provided for the prompt, coordinated actions needed to control the epidemic.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The largest outbreak of hand; foot and mouth disease in Singapore in 2008: the role of enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A strains.Int J Infect Dis. 2010 Dec;14(12):e1076-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2010.07.006. Epub 2010 Oct 16. Int J Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20952237
-
Hand, foot and mouth disease in Singapore: a comparison of fatal and non-fatal cases.Acta Paediatr. 2003 Oct;92(10):1163-9. Acta Paediatr. 2003. PMID: 14632332
-
Epidemiological and etiological characteristics of hand, foot, and mouth disease in Ningbo, China, 2008-2011.J Clin Virol. 2012 Aug;54(4):342-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2012.04.021. Epub 2012 May 30. J Clin Virol. 2012. PMID: 22652041
-
[Prevalence and Analyses of the Changing Etiology of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease in China].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2015 Sep;31(5):554-9. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26738295 Review. Chinese.
-
EV71: an emerging infectious disease vaccine target in the Far East?Vaccine. 2010 Apr 30;28(20):3516-21. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.03.003. Epub 2010 Mar 19. Vaccine. 2010. PMID: 20304038 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a pseudovirus-based assay for measuring neutralizing antibodies against Coxsackievirus A10.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020 Jun 2;16(6):1434-1440. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1691404. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020. PMID: 31851566 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of temperature on childhood hand, foot and mouth disease in Guangdong Province, China, 2010-2013: a multicity study.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Nov 12;19(1):969. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4594-y. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31718560 Free PMC article.
-
Current status of hand-foot-and-mouth disease.J Biomed Sci. 2023 Feb 24;30(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12929-023-00908-4. J Biomed Sci. 2023. PMID: 36829162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different responses of weather factors on hand, foot and mouth disease in three different climate areas of Gansu, China.BMC Infect Dis. 2018 Jan 8;18(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2860-4. BMC Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29310596 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase-3 Inhibition Attenuates the Cytopathic Effects of EV71 Infection.Front Microbiol. 2018 Apr 26;9:817. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00817. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29755438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Melnick JL. Enteroviruses: polioviruses, coxsackieviruses, echoviruses, and newer enteroviruses. In: Fields BN, Knipe DM, Howley PM, Chanlock RM, Melnick JL, Monath TP, et al., editors. Field’s virology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven Publishers; 1996. p. 655–712.
-
- Tunnessen WW Jr. Erythema infectiosum, roseola, and enteroviral exanthems. In: Gorbach SL, Bartlett JG, Blacklow NR, editors. Infectious diseases. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Company; 1992. p. 1120–5.
-
- Chan MCK, Wong HB. Hand-foot and mouth disease. J Singapore Paediatr Soc. 1973;15:31–4.
-
- Tay CH, Gaw CYN, Low T, Ong C, Chia KW, Yeo H, et al. Outbreak of hand, foot and mouth disease in Singapore. Singapore Med J. 1974;15:174–83.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
