STAT5a activation mediates the epithelial to mesenchymal transition induced by oncogenic RhoA
- PMID: 12529425
- PMCID: PMC140226
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-08-0454
STAT5a activation mediates the epithelial to mesenchymal transition induced by oncogenic RhoA
Abstract
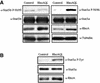
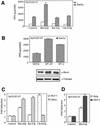
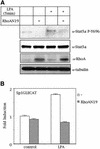
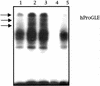
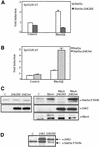
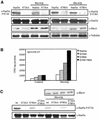
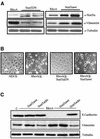
The involvement of Rho GTPases in signal transduction pathways leading to transcription activation is one of the major roles of this family of GTPases. Thus, the identification of transcription factors regulated by Rho GTPases and the understanding of the mechanisms of their activation and its biological outcome are of great interest. Here, we provide evidence that Rho GTPases modulate Stat5a, a transcription factor of the family of signal transducers and activators of transcription. RhoA triggers tyrosine phosphorylation (Y696) of Stat5a via a JAK2-dependent mechanism and promotes DNA-binding activity of Stat5a. Tyrosine phosphorylation of Stat5a is also stimulated physiologically by lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) in a Rho-dependent manner. Simultaneously, RhoA reduces serine phosphorylation of Stat5a at both serine residues S726 and S780, resulting in a further increase of activity as defined by mutagenesis experiments. Furthermore, serine dephosphorylation of Stat5a by RhoA does not take place by down-modulation of either JNK1, MEK1, or p38 MAP kinases, as determined by transfection experiments or chemical inhibition of both MEK1, p38, and JNK serine kinases. Thus, RhoA regulates Stat5a via tyrosine phosphorylation and via a yet to be determined novel down-modulating pathway that involves serine dephosphorylation. Finally, we provide evidence for a role of Stat5a in RhoA-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition with concomitant increase in vimentin expression, E-cadherin down-regulation, and cell motility.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Simultaneous tyrosine and serine phosphorylation of STAT3 transcription factor is involved in Rho A GTPase oncogenic transformation.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Oct;12(10):3282-94. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.10.3282. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11598209 Free PMC article.
-
Dominant negative variants of the SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatase inhibit prolactin activation of Jak2 (janus kinase 2) and induction of Stat5 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 5)-dependent transcription.Mol Endocrinol. 1998 Apr;12(4):556-67. doi: 10.1210/mend.12.4.0086. Mol Endocrinol. 1998. PMID: 9544991
-
Integrin-mediated adhesion of endothelial cells induces JAK2 and STAT5A activation: role in the control of c-fos gene expression.Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Oct;10(10):3463-71. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.10.3463. Mol Biol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10512880 Free PMC article.
-
STAT5A interacts with and is phosphorylated upon activation of the mu-opioid receptor.J Neurochem. 2005 May;93(4):918-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03069.x. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 15857395
-
Prolactin regulation of estrogen receptor expression.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2003 Apr;14(3):118-23. doi: 10.1016/s1043-2760(03)00030-4. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2003. PMID: 12670737 Review.
Cited by
-
Rac1 links integrin-mediated adhesion to the control of lactational differentiation in mammary epithelia.J Cell Biol. 2006 Jun 5;173(5):781-93. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200601059. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16754961 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced RhoA expression enhances breast cancer metastasis with a concomitant increase in CCR5 and CXCR4 chemokines signaling.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 8;9(1):16351. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52746-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31705019 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophosphatidic Acid disrupts junctional integrity and epithelial cohesion in ovarian cancer cells.J Oncol. 2012;2012:501492. doi: 10.1155/2012/501492. Epub 2012 Apr 22. J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22593767 Free PMC article.
-
Essential role of STAT5a in DCIS formation and invasion following estrogen treatment.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Aug 5;12(14):15104-15120. doi: 10.18632/aging.103586. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32633727 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 contributes to tumor growth, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor targeting.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Dec 1;14(23):7682-90. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1328. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19047094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alberts AS, Geneste O, Treisman R. Activation of SRF-regulated chromosomal templates by Rho-family GTPases requires a signal that also induces H4 hyperacetylation. Cell. 1998;92:475–487. - PubMed
-
- Al-Shami A, Mahanna W, Naccache PH. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-activated signaling pathways in human neutrophils: selective activation of Jak2, Stat3, and Stat5b. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:1058–1063. - PubMed
-
- Aznar S, Lacal JC. Searching new targets for anticancer drug design: the families of Ras and RhoGTPases and their effectors. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001a;67:193–234. - PubMed
-
- Aznar S, Lacal JC. Rho signals to cell growth and apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2001b;165:1–10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

