iProClass: an integrated database of protein family, function and structure information
- PMID: 12520030
- PMCID: PMC165491
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg044
iProClass: an integrated database of protein family, function and structure information
Abstract
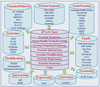
The iProClass database provides comprehensive, value-added descriptions of proteins and serves as a framework for data integration in a distributed networking environment. The protein information in iProClass includes family relationships as well as structural and functional classifications and features. The current version consists of about 830 000 non-redundant PIR-PSD, SWISS-PROT, and TrEMBL proteins organized with more than 36 000 PIR superfamilies, 145 000 families, 4000 domains, 1300 motifs and 550 000 FASTA similarity clusters. It provides rich links to over 50 database of protein sequences, families, functions and pathways, protein-protein interactions, post-translational modifications, protein expressions, structures and structural classifications, genes and genomes, ontologies, literature and taxonomy. Protein and superfamily summary reports present extensive annotation information and include membership statistics and graphical display of domains and motifs. iProClass employs an open and modular architecture for interoperability and scalability. It is implemented in the Oracle object-relational database system and is updated biweekly. The database is freely accessible from the web site at http://pir.georgetown.edu/iproclass/ and searchable by sequence or text string. The data integration in iProClass supports exploration of protein relationships. Such knowledge is fundamental to the understanding of protein evolution, structure and function and crucial to functional genomic and proteomic research.
Similar articles
-
iProClass: an integrated, comprehensive and annotated protein classification database.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Jan 1;29(1):52-4. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.1.52. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11125047 Free PMC article.
-
The Protein Information Resource: an integrated public resource of functional annotation of proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):35-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.35. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 11752247 Free PMC article.
-
The Protein Information Resource.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jan 1;31(1):345-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg040. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12520019 Free PMC article.
-
Protein family classification and functional annotation.Comput Biol Chem. 2003 Feb;27(1):37-47. doi: 10.1016/s1476-9271(02)00098-1. Comput Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12798038 Review.
-
Update on genome completion and annotations: Protein Information Resource.Hum Genomics. 2004 Mar;1(3):229-33. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-1-3-229. Hum Genomics. 2004. PMID: 15588483 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transforming Clinical Research: The Power of High-Throughput Omics Integration.Proteomes. 2024 Sep 6;12(3):25. doi: 10.3390/proteomes12030025. Proteomes. 2024. PMID: 39311198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DASMI: exchanging, annotating and assessing molecular interaction data.Bioinformatics. 2009 May 15;25(10):1321-8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp142. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19420069 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Bioinformatics Infrastructure for the Integration and Analysis of Multiple High-Throughput "omics" Data.Adv Bioinformatics. 2010;2010:423589. doi: 10.1155/2010/423589. Epub 2010 Mar 29. Adv Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20369061 Free PMC article.
-
Towards an understanding of wheat chloroplasts: a methodical investigation of thylakoid proteome.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 May;39(5):5069-83. doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-1302-4. Epub 2011 Dec 11. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22160430
-
A Chronic Fatigue Syndrome - related proteome in human cerebrospinal fluid.BMC Neurol. 2005 Dec 1;5:22. doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-5-22. BMC Neurol. 2005. PMID: 16321154 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu C.H., Huang,H., Arminski,L., Castro-Alvear,J., Chen,Y., Hu,Z., Ledley,R.S., Lewis,K.C., Mewes,H.-W., Orcutt,B.C., Suzek,B., Tsugita,A., Vinayaka,C.R., Yeh,L.-S., Zhang,J. and Barker,W.C. (2002) The Protein Information Resource: an integrated public resource of functional annotation of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res., 30, 35–37. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barker W.C., Pfeiffer,F. and George,D.G. (1996) Superfamily classification in PIR-International Protein Sequence Database. Methods Enzymol., 266, 59–71. - PubMed