Critical role of the carboxyl terminus of proline-rich tyrosine kinase (Pyk2) in the activation of human neutrophils by tumor necrosis factor: separation of signals for the respiratory burst and degranulation
- PMID: 12515814
- PMCID: PMC2193795
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20021638
Critical role of the carboxyl terminus of proline-rich tyrosine kinase (Pyk2) in the activation of human neutrophils by tumor necrosis factor: separation of signals for the respiratory burst and degranulation
Abstract
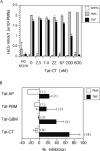
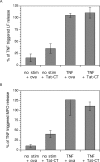
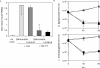
Transduction of Tat-tagged fusion proteins confirmed a hypothesis based on pharmacologic inhibitors (Fuortes, M., M. Melchior, H. Han, G.J. Lyon, and C. Nathan. 1999. J. Clin. Invest. 104:327-335) that proline-rich tyrosine kinase (Pyk2) plays a critical role in the activation of adherent human neutrophils, and allowed an analysis of individual Pyk2 domains not possible with chemical inhibitors. Acting as a dominant negative, the COOH terminus of Pyk2 fused to a Tat peptide (Tat-CT), but not other regions of Pyk2, specifically inhibited the respiratory burst of cells responding to tumor necrosis factor (TNF), Salmonella, or Listeria, while sparing responses induced by phorbol ester. Tat-CT suppressed TNF-triggered cell spreading and the phosphorylation of endogenous Pyk2 and the associated tyrosine kinase Syk without blocking the ability of neutrophils to degranulate and kill bacteria. Thus, separate signals control the respiratory burst and degranulation, and a normal rate of killing of some bacteria can be sustained by granule products in conjunction with a minimal residual respiratory burst. Inhibition of select inflammatory functions without impairment of antibacterial activity may commend the Pyk2 pathway as a potential target for antiinflammatory therapy.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Chemical inhibitors of TNF signal transduction in human neutrophils point to distinct steps in cell activation.J Leukoc Biol. 2006 Jan;79(1):147-54. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0605308. Epub 2005 Nov 7. J Leukoc Biol. 2006. PMID: 16275893
-
Role of the tyrosine kinase pyk2 in the integrin-dependent activation of human neutrophils by TNF.J Clin Invest. 1999 Aug;104(3):327-35. doi: 10.1172/JCI6018. J Clin Invest. 1999. PMID: 10430614 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 in reversion of the adhesion-mediated suppression of reactive oxygen species generation by human neutrophils.J Immunol. 2005 Jun 15;174(12):8049-55. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.12.8049. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15944312
-
Beta2 integrin-dependent phosphorylation of protein-tyrosine kinase Pyk2 stimulated by tumor necrosis factor alpha and fMLP in human neutrophils adherent to fibrinogen.FEBS Lett. 1999 May 14;451(1):33-8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00539-6. FEBS Lett. 1999. PMID: 10356979
-
Involvement of proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 in platelet activation: tyrosine phosphorylation mostly dependent on alphaIIbbeta3 integrin and protein kinase C, translocation to the cytoskeleton and association with Shc through Grb2.Biochem J. 2000 Apr 15;347(Pt 2):561-9. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3470561. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 10749687 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hematopoietic Pyk2 regulates migration of differentiated HL-60 cells.J Inflamm (Lond). 2010 May 27;7:26. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-7-26. J Inflamm (Lond). 2010. PMID: 20507587 Free PMC article.
-
Src-family and Syk kinases in activating and inhibitory pathways in innate immune cells: signaling cross talk.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 Mar 1;3(3):a002352. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002352. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011. PMID: 21068150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of neutrophil functions by proinflammatory cytokines.Int J Hematol. 2006 Oct;84(3):205-9. doi: 10.1532/IJH97.06141. Int J Hematol. 2006. PMID: 17050192 Review.
-
Activation of human neutrophils by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and tumor necrosis factor alpha: role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.Int J Hematol. 2004 Dec;80(5):421-7. doi: 10.1532/ijh97.04122. Int J Hematol. 2004. PMID: 15646653
-
Calcium-sensing soluble adenylyl cyclase mediates TNF signal transduction in human neutrophils.J Exp Med. 2005 Aug 1;202(3):353-61. doi: 10.1084/jem.20050778. Epub 2005 Jul 25. J Exp Med. 2005. PMID: 16043520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klebanoff, S.J., M.A. Vadas, J.M. Harlan, L.H. Sparks, J.R. Gamble, J.M. Agosti, and A.M. Waltersdorph. 1986. Stimulation of neutrophils by tumor necrosis factor. J. Immunol. 136:4220–4225. - PubMed
-
- Nathan, C.F. 1989. Respiratory burst in adherent human neutrophils: triggering by colony-stimulating factors CSF-GM and CSF-G. Blood. 73:301–306. - PubMed
-
- De La Harpe, J., and C.F. Nathan. 1989. Adenosine regulates the respiratory burst of cytokine-triggered human neutrophils adherent to biologic surfaces. J. Immunol. 143:596–602. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

