The Ras/Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway induces autocrine-paracrine growth inhibition via the leukemia inhibitory factor/JAK/STAT pathway
- PMID: 12509453
- PMCID: PMC151536
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.2.543-554.2003
The Ras/Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway induces autocrine-paracrine growth inhibition via the leukemia inhibitory factor/JAK/STAT pathway
Abstract
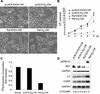
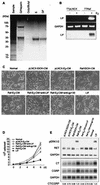
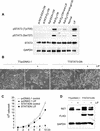
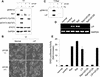
Sustained activation of the Ras/Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway can lead to cell cycle arrest in many cell types. We have found, with human medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) cells, that activated Ras or c-Raf-1 can induce growth arrest by producing and secreting an autocrine-paracrine factor. This protein was purified from cell culture medium conditioned by Raf-activated MTC cells and was identified by mass spectrometry as leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF). LIF expression upon Raf activation and subsequent activation of JAK-STAT3 was also observed in small cell lung carcinoma cells, suggesting that this autocrine-paracrine signaling may be a common response to Ras/Raf activation. LIF was sufficient to induce growth arrest and differentiation of MTC cells. This effect was mediated through the gp130/JAK/STAT3 pathway, since anti-gp130 blocking antibody or dominant-negative STAT3 blocked the effects of LIF. Thus, LIF expression provides a novel mechanism allowing Ras/Raf signaling to activate the JAK-STAT3 pathway. In addition to this cell-extrinsic growth inhibitory pathway, we find that the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway induces an intracellular growth inhibitory signal, independent of the LIF/JAK/STAT3 pathway. Therefore, activation of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway can lead to growth arrest and differentiation via at least two different signaling pathways. This use of multiple pathways may be important for "fail-safe" induction and maintenance of cell cycle arrest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IFI16 is an essential mediator of growth inhibition, but not differentiation, induced by the leukemia inhibitory factor/JAK/STAT pathway in medullary thyroid carcinoma cells.J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 11;280(6):4913-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410542200. Epub 2004 Nov 30. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15572361
-
Leukemia inhibitory factor can mediate Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK-induced growth inhibitory signaling in medullary thyroid cancer cells.Cancer Lett. 2010 Nov 1;297(1):31-41. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.04.021. Epub 2010 May 31. Cancer Lett. 2010. PMID: 20570039
-
Interleukin-1beta can mediate growth arrest and differentiation via the leukemia inhibitory factor/JAK/STAT pathway in medullary thyroid carcinoma cells.Cytokine. 2005 Feb 7;29(3):125-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2004.10.005. Epub 2004 Dec 1. Cytokine. 2005. PMID: 15613280
-
Signalling, cell cycle and pluripotency in embryonic stem cells.Trends Cell Biol. 2002 Sep;12(9):432-8. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(02)02352-8. Trends Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12220864 Review.
-
Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Aug;1773(8):1263-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.10.001. Epub 2006 Oct 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17126425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel U-STAT3-dependent mechanism mediates the deleterious effects of chronic nicotine exposure on renal injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Mar 15;302(6):F722-9. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00338.2011. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22169004 Free PMC article.
-
Focal adhesion kinase, a downstream mediator of Raf-1 signaling, suppresses cellular adhesion, migration, and neuroendocrine markers in BON carcinoid cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2010 May;8(5):775-82. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0525. Epub 2010 Apr 20. Mol Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20407018 Free PMC article.
-
The Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway can mediate growth inhibitory and differentiation signaling via androgen receptor downregulation in prostate cancer cells.Exp Cell Res. 2011 Nov 1;317(18):2671-82. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2011.08.008. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Exp Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21871886 Free PMC article.
-
Three LIF-dependent signatures and gene clusters with atypical expression profiles, identified by transcriptome studies in mouse ES cells and early derivatives.BMC Genomics. 2009 Feb 9;10:73. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-73. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19203379 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour cells expressing single VEGF isoforms display distinct growth, survival and migration characteristics.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 13;9(8):e104015. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104015. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25119572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aubert, J., S. Dessolin, N. Belmonte, M. Li, F. R. McKenzie, L. Staccini, P. Villageois, B. Barhanin, A. Vernallis, A. G. Smith, G. Ailhaud, and C. Dani. 1999. Leukemia inhibitory factor and its receptor promote adipocyte differentiation via the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. J. Biol. Chem. 274:24965-24972. - PubMed
-
- Auernhammer, C. J., V. Chesnokova, and S. Melmed. 1998. Leukemia inhibitory factor modulates interleukin-1Â-induced activation of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis. Endocrinology 139:2201-2208. - PubMed
-
- Auernhammer, C. J., and S. Melmed. 2000. Leukemia inhibitory factor-neuroimmune modulater of endocrine function. Endocr. Rev. 21:313-345. - PubMed
-
- Blalock, W. L., P. W. Moye, F. Chang, M. Pearce, L. S. Steelman, M. McMahon, and J. A. McCubrey. 2000. Combined effects of aberrant MEK1 activity and BCL2 overexpression on relieving the cytokine dependency of human and murine hematopoietic cells. Leukemia 14:1080-1096. - PubMed
-
- Blalock, W. L., M. Pearce, F. Chang, J. T. Lee, S. C. Pohnert, C. Burrows, L. S. Steelman, R. A. Franklin, M. McMahon, and J. A. McCubrey. 2001. Effects of inducible MEK1 activation on the cytokine dependency of lymphoid cells. Leukemia 15:794-807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
