Regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor expression by glucocorticoids in vivo
- PMID: 12507889
- PMCID: PMC1851131
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63797-2
Regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor expression by glucocorticoids in vivo
Abstract
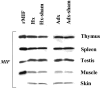
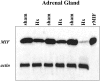
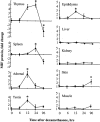
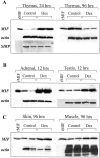
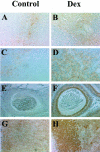
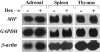
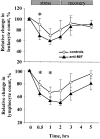
Glucocorticoid hormones are important anti-inflammatory agents because of their anti-inflammatory and proapoptotic action within the immune system. Their clinical usefulness remains limited however by side effects that result in part from their growth inhibitory action on sensitive target tissues. The protein mediator, macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), is an important regulator of the host immune response and exhibits both glucocorticoid-antagonistic and growth-regulatory properties. MIF has been shown to contribute significantly to the development of immunopathology in several models of inflammatory disease. Although there is emerging evidence for a functional interaction between MIF and glucocorticoids in vitro, little is known about their reciprocal influence in vivo. We investigated the expression of MIF in rat tissues after ablation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and after high-dose glucocorticoid administration. MIF expression is constitutive and independent of the influence of adrenal hormones. Hypophysectomy and the attendent loss of pituitary hormones, by contrast, decreased MIF protein content in the adrenal gland. Administration of dexamethasone was found to increase MIF protein expression in those organs that are considered to be sensitive to the growth inhibitory effects of glucocorticoids (immune and endocrine tissues, skin, and muscle). This increase was most likely because of a posttranscriptional regulatory effect because tissue MIF mRNA levels were not influenced by dexamethasone treatment. Finally, MIF immunoneutralization enhanced lymphocyte egress from blood during stress-induced lymphocyte redistribution, consistent with a functional interaction between MIF and glucocorticoids on immune cell trafficking in vivo. These findings suggest a role for MIF in both the homeostatic and physiological action of glucocorticoids in vivo.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Migration inhibitory factor expression in experimentally induced endotoxemia.Am J Pathol. 1997 Jan;150(1):235-46. Am J Pathol. 1997. PMID: 9006339 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of macrophage migration inhibitory factor by endogenous glucocorticoids in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Apr;43(4):827-33. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200004)43:4<827::AID-ANR13>3.0.CO;2-K. Arthritis Rheum. 2000. PMID: 10765927
-
Response of serum macrophage migration inhibitory factor levels to stimulation or suppression of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis in normal subjects and patients with Cushing's disease.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Apr;87(4):1834-40. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.4.8382. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. PMID: 11932327
-
Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF): A Glucocorticoid Counter-Regulator within the Immune System.Crit Rev Immunol. 2017;37(2-6):359-370. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.v37.i2-6.90. Crit Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29773026 Review.
-
Glucocorticoids and macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) are neuroendocrine modulators of inflammation and neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury.Semin Immunol. 2014 Oct;26(5):409-14. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2014.03.004. Epub 2014 Apr 24. Semin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24768088 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of differentially expressed genes with activation of mouse hepatic stellate cells by high-density cDNA microarray.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Jun 1;10(11):1600-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i11.1600. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15162533 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal patterns of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (Mif) expression in the mouse placenta.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2010 Aug 4;8:95. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-8-95. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20684790 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and functionally-related genes, D-DT, CD74, CD44, CXCR2 and CXCR4, in glioblastoma.Oncol Lett. 2018 Sep;16(3):2881-2886. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8990. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30127875 Free PMC article.
-
The Golgi-associated protein p115 mediates the secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor.J Immunol. 2009 Jun 1;182(11):6896-906. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803710. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19454686 Free PMC article.
-
The role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in autoimmune liver disease.Hepatology. 2014 Feb;59(2):580-91. doi: 10.1002/hep.26664. Epub 2013 Dec 20. Hepatology. 2014. PMID: 23913513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Swope MD, Lolis E: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: cytokine, hormone, or enzyme? Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 1999, 139:1-32 - PubMed
-
- Bloom BR, Bennett B: Mechanism of a reaction in vitro associated with delayed-type hypersensitivity. Science 1966, 111:514-521 - PubMed
-
- Metz CN, Bucala R: MIF. 2000:pp 703-716 Academic Press, San Diego CA
-
- Bernhagen J, Calandra T, Cerami A, Bucala R: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is a neuroendocrine mediator of endotoxaemia. Trends Microbiol 1994, 2:198-201 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

