Infection of cells expressing CXCR4 mutants lacking N-glycosylation at the N-terminal extracellular domain is enhanced for R5X4-dualtropic human immunodeficiency virus type-1
- PMID: 12489987
- PMCID: PMC139973
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-2-31
Infection of cells expressing CXCR4 mutants lacking N-glycosylation at the N-terminal extracellular domain is enhanced for R5X4-dualtropic human immunodeficiency virus type-1
Abstract
Background: Infection with human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) requires binding of the viral envelope gp120 to CD4 and to the CXCR4 coreceptor. Both, gp120 and CXCR4 are subject to N-glycosylation. Here we investigated the influence of the N-linked glycans g1 and g2 present on CXCR4 for HIV-1 infection.
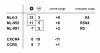
Methods: The two CXCR4 N-glycosylation sites g1 (NYT) and g2 (NVS) were mutated by changing the first or third amino acids N or T/S to Q and A respectively (g1; N11Q or T13A; g2, N176Q or S178A). Human osteosarcoma cells (GHOST) expressing human CD4 and the various CXCR4 glycosylation mutants were tested for infection using NL4-3-based viruses with X4, R5 or R5X4-tropism differing only in the V3 loop region.
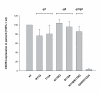
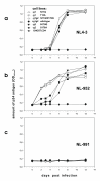
Results: All constructed cell lines expressing the various CXCR4 glycomutants showed similar permissiveness for the X4-monotropic virus and no change in the coreceptor specificity that allows infection of a CCR5-dependent R5-monotropic virus. Interestingly, the removal of glycan g1 significantly enhanced the permissiveness of GHOST cells for the R5X4 dualtropic virus. GHOST cells expressing the CXCR4-g1 or CXCR4-g1/2 mutants were infected at higher rates by the R5X4-dualtropic virus compared to cells expressing CXCR4-wt or CXCR4-g2 coreceptors.
Conclusion: Our present observations underscore a role for glycans present on the CXCR4 coreceptor in the entry process of HIV-1. The data will help to better understand the multifaceted mechanism of HIV infection and the selective forces which drive HIV-1 evolution from mono- to dual-tropism.
Figures


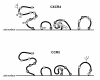
 ), lysine (K) and arginine (R) amino acid residues, Symbol minus (
), lysine (K) and arginine (R) amino acid residues, Symbol minus ( ), glutamic (E) and aspartic (D) acid amino acid residues. Boxed, amino acids related to coreceptor usage
), glutamic (E) and aspartic (D) acid amino acid residues. Boxed, amino acids related to coreceptor usageSimilar articles
-
The N-linked glycan g15 within the V3 loop of the HIV-1 external glycoprotein gp120 affects coreceptor usage, cellular tropism, and neutralization.Virology. 2002 Dec 5;304(1):70-80. doi: 10.1006/viro.2002.1760. Virology. 2002. PMID: 12490404
-
Differences in molecular evolution between switch (R5 to R5X4/X4-tropic) and non-switch (R5-tropic only) HIV-1 populations during infection.Infect Genet Evol. 2010 Apr;10(3):356-64. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2009.05.003. Epub 2009 May 14. Infect Genet Evol. 2010. PMID: 19446658
-
Complex determinants in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope gp120 mediate CXCR4-dependent infection of macrophages.J Virol. 2005 Nov;79(21):13250-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.21.13250-13261.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16227248 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of HIV-1 subtype and tropism on treatment with chemokine coreceptor entry inhibitors; overview of viral entry inhibition.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2015;41(4):473-87. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2013.867829. Epub 2014 Mar 17. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 24635642 Review.
-
CXCR4 Is a Potential Target for Anti-HIV Gene Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 18;25(2):1187. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021187. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256260 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of CXCR4 signaling.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Apr;1768(4):952-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.11.002. Epub 2006 Nov 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17169327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conformational HIV-1 envelope on particulate structures: a tool for chemokine coreceptor binding studies.J Transl Med. 2011 Jan 27;9 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S1. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-S1-S1. J Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 21284899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemokine receptor internalization and intracellular trafficking.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005 Dec;16(6):637-58. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2005.05.008. Epub 2005 Jul 5. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005. PMID: 15998596 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Feng Y, Broder CC, Kennedy PE, Berger EA. HIV-1 entry cofactor: functional cDNA cloning of a seven-transmembrane, G protein-coupled receptor. Science. 1996;272:872–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

