XRCC2 is Required for the Formation of Rad51 Foci Induced by Ionizing Radiation and DNA Cross-Linking Agent Mitomycin C
- PMID: 12488590
- PMCID: PMC153789
- DOI: 10.1155/S1110724302204040
XRCC2 is Required for the Formation of Rad51 Foci Induced by Ionizing Radiation and DNA Cross-Linking Agent Mitomycin C
Abstract
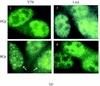
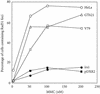
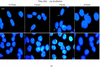
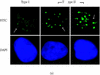
XRCC2 protein shares weak amino acid sequence similarity with Rad51, which is a central player in homologous recombinational repair (HRR). Rad51 proteins assemble at the sites of HRR and form visible nuclear foci in response to DNA damage. Xrcc2 hamster mutant irs1 cells are incapable of forming Rad51 foci after ionizing irradiation or DNA cross-linking agent mitomycin C treatment, though the Rad51 protein level is normal in the mutant. The defect can be corrected in an XRCC2 transformant. Time course study showed that the irs1 cells primarily lacked the early response (2 hours after irradiation) to form small Rad51 foci (type 1) and later response (8 hours after irradiation) to form large foci (type 2). These results suggested that XRCC2 is essential for the assembly of the DNA damage-induced Rad51 foci and that XRCC2 may play an important role in the early stage of HRR.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Differential roles of XRCC2 in homologous recombinational repair of stalled replication forks.J Cell Biochem. 2005 Aug 1;95(5):942-54. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20457. J Cell Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15861395
-
XRCC2 is a nuclear RAD51-like protein required for damage-dependent RAD51 focus formation without the need for ATP binding.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jun 22;276(25):22148-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M102396200. Epub 2001 Apr 11. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11301337
-
XRCC2 (X-ray repair cross complementing 2).Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2019 Jan;23(1):1-7. doi: 10.4267/2042/69759. Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2019. PMID: 31275435 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of XRCC2 in RAD51-related DNA damage repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2010 May 4;9(5):517-25. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.01.016. Epub 2010 Feb 26. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010. PMID: 20189471
-
The contribution of homologous recombination in preserving genome integrity in mammalian cells.Biochimie. 1999 Jan-Feb;81(1-2):87-105. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(99)80042-x. Biochimie. 1999. PMID: 10214914 Review.
Cited by
-
Widespread genomic breaks generated by activation-induced cytidine deaminase are prevented by homologous recombination.Nat Immunol. 2010 Sep;11(9):820-6. doi: 10.1038/ni.1909. Epub 2010 Jul 25. Nat Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20657597 Free PMC article.
-
Counting the cost of public and philanthropic R&D funding: the case of olaparib.J Pharm Policy Pract. 2022 Aug 16;15(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s40545-022-00445-9. J Pharm Policy Pract. 2022. PMID: 35974344 Free PMC article.
-
Formation and repair of interstrand cross-links in DNA.Chem Rev. 2006 Feb;106(2):277-301. doi: 10.1021/cr040478b. Chem Rev. 2006. PMID: 16464006 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
DNA repair pathways in trypanosomatids: from DNA repair to drug resistance.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2014 Mar;78(1):40-73. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00045-13. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24600040 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baumann P, Benson F E, West S C. Human Rad51 protein promotes ATP-dependent homologous pairing and strand transfer reactions in vitro. Cell. 1996;87(4):757–766. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya A, Ear U S, Koller B H, Weichselbaum R R, Bishop D K. The breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1 is required for subnuclear assembly of Rad51 and survival following treatment with the DNA cross-linking agent cisplatin. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(31):23899–23903. - PubMed
-
- Bishop D K. RecA homologs Dmc1 and Rad51 interact to form multiple nuclear complexes prior to meiotic chromosome synapsis. Cell. 1994;79(6):1081–1092. - PubMed
-
- Bishop D K, Ear U, Bhattacharyya A. Xrcc3 is required for assembly of Rad51 complexes in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(34):21482–21488. - PubMed
-
- Braybrooke J P, Spink K G, Thacker J, Hickson I D. The RAD51 family member, RAD51L3, is a DNA-stimulated ATPase that forms a complex with XRCC2. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(37):29100–29106. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

