Efficient targeting of protein antigen to the dendritic cell receptor DEC-205 in the steady state leads to antigen presentation on major histocompatibility complex class I products and peripheral CD8+ T cell tolerance
- PMID: 12486105
- PMCID: PMC2196060
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20021598
Efficient targeting of protein antigen to the dendritic cell receptor DEC-205 in the steady state leads to antigen presentation on major histocompatibility complex class I products and peripheral CD8+ T cell tolerance
Abstract
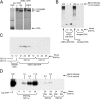
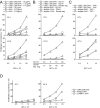
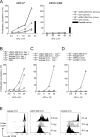
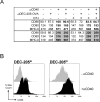
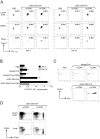
To identify endocytic receptors that allow dendritic cells (DCs) to capture and present antigens on major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I products in vivo, we evaluated DEC-205, which is abundant on DCs in lymphoid tissues. Ovalbumin (OVA) protein, when chemically coupled to monoclonal alphaDEC-205 antibody, was presented by CD11c+ lymph node DCs, but not by CD11c- cells, to OVA-specific, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Receptor-mediated presentation was at least 400 times more efficient than unconjugated OVA and, for MHC class I, the DCs had to express transporter of antigenic peptides (TAP) transporters. When alphaDEC-205:OVA was injected subcutaneously, OVA protein was identified over a 4-48 h period in DCs, primarily in the lymph nodes draining the injection site. In vivo, the OVA protein was selectively presented by DCs to TCR transgenic CD8+ cells, again at least 400 times more effectively than soluble OVA and in a TAP-dependent fashion. Targeting of alphaDEC-205:OVA to DCs in the steady state initially induced 4-7 cycles of T cell division, but the T cells were then deleted and the mice became specifically unresponsive to rechallenge with OVA in complete Freund's adjuvant. In contrast, simultaneous delivery of a DC maturation stimulus via CD40, together with alphaDEC-205:OVA, induced strong immunity. The CD8+ T cells responding in the presence of agonistic alphaCD40 antibody produced large amounts of interleukin 2 and interferon gamma, acquired cytolytic function in vivo, emigrated in large numbers to the lung, and responded vigorously to OVA rechallenge. Therefore, DEC-205 provides an efficient receptor-based mechanism for DCs to process proteins for MHC class I presentation in vivo, leading to tolerance in the steady state and immunity after DC maturation.
Figures
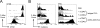

Similar articles
-
In vivo targeting of antigens to maturing dendritic cells via the DEC-205 receptor improves T cell vaccination.J Exp Med. 2004 Mar 15;199(6):815-24. doi: 10.1084/jem.20032220. J Exp Med. 2004. PMID: 15024047 Free PMC article.
-
Carbohydrate-mediated targeting of antigen to dendritic cells leads to enhanced presentation of antigen to T cells.Chembiochem. 2008 Jan 25;9(2):294-303. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200700310. Chembiochem. 2008. PMID: 18186095 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Conjugation of a Purified DEC-205-Directed Antibody with Full-Length Protein for Targeting Mouse Dendritic Cells In Vitro and In Vivo.J Vis Exp. 2021 Feb 5;(168). doi: 10.3791/62018. J Vis Exp. 2021. PMID: 33616089
-
Tolerogenic dendritic cells.Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:685-711. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.21.120601.141040. Epub 2001 Dec 19. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12615891 Review.
-
Endocytic Recycling of MHC Class I Molecules in Non-professional Antigen Presenting and Dendritic Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 7;9:3098. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03098. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30666258 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HLA-A2.1-restricted ECM1-derived epitope LA through DC cross-activation priming CD8+ T and NK cells: a novel therapeutic tumour vaccine.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Apr 28;14(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01081-7. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33910591 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-presentation of IgG-containing immune complexes.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Apr;70(8):1319-34. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1100-8. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 22847331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tolerogenic Donor-Derived Dendritic Cells Risk Sensitization In Vivo owing to Processing and Presentation by Recipient APCs.J Immunol. 2013 May 1;190(9):4848-60. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200870. Epub 2013 Mar 27. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23536635 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow dendritic cell-mediated regulation of TLR and B cell receptor signaling in B cells.J Immunol. 2012 Oct 1;189(7):3355-67. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101352. Epub 2012 Aug 31. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22942427 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen-loaded pH-sensitive hydrogel microparticles are taken up by dendritic cells with no requirement for targeting antibodies.Integr Biol (Camb). 2013 Jan;5(1):195-203. doi: 10.1039/c2ib20109g. Integr Biol (Camb). 2013. PMID: 23060228 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kappler, J.W., N. Roehm, and P. Marrack. 1987. T cell tolerance by clonal elimination in the thymus. Cell. 49:273–280. - PubMed
-
- Kisielow, P., H. Bluthmann, U.D. Staerz, M. Steinmetz, and H. von Boehmer. 1988. Tolerance in T-cell-receptor transgenic mice involves deletion of nonmature CD4+8+ thymocytes. Nature. 333:742–746. - PubMed
-
- Bouneaud, C., P. Kourilsky, and P. Bousso. 2000. Impact of negative selection on the T cell repertoire reactive to a self-peptide: a large fraction of T cell clones escapes clonal detection. Immunity. 13:829–840. - PubMed
-
- Matzinger, P., and S. Guerder. 1989. Does T-cell tolerance require a dedicated antigen-presenting cell? Nature. 338:74–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

