Role of RAD52 epistasis group genes in homologous recombination and double-strand break repair
- PMID: 12456786
- PMCID: PMC134659
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.66.4.630-670.2002
Role of RAD52 epistasis group genes in homologous recombination and double-strand break repair
Abstract
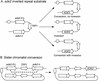
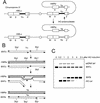
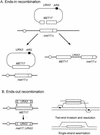
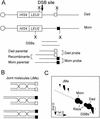
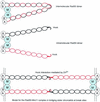
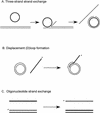
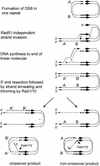
The process of homologous recombination is a major DNA repair pathway that operates on DNA double-strand breaks, and possibly other kinds of DNA lesions, to promote error-free repair. Central to the process of homologous recombination are the RAD52 group genes (RAD50, RAD51, RAD52, RAD54, RDH54/TID1, RAD55, RAD57, RAD59, MRE11, and XRS2), most of which were identified by their requirement for the repair of ionizing-radiation-induced DNA damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The Rad52 group proteins are highly conserved among eukaryotes, and Rad51, Mre11, and Rad50 are also conserved in prokaryotes and archaea. Recent studies showing defects in homologous recombination and double-strand break repair in several human cancer-prone syndromes have emphasized the importance of this repair pathway in maintaining genome integrity. Although sensitivity to ionizing radiation is a universal feature of rad52 group mutants, the mutants show considerable heterogeneity in different assays for recombinational repair of double-strand breaks and spontaneous mitotic recombination. Herein, I provide an overview of recent biochemical and structural analyses of the Rad52 group proteins and discuss how this information can be incorporated into genetic studies of recombination.
Figures







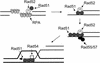
Similar articles
-
Recombination proteins in yeast.Annu Rev Genet. 2004;38:233-71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.38.072902.091500. Annu Rev Genet. 2004. PMID: 15568977 Review.
-
Transcriptional profile of the homologous recombination machinery and characterization of the EhRAD51 recombinase in response to DNA damage in Entamoeba histolytica.BMC Mol Biol. 2008 Apr 10;9:35. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-9-35. BMC Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18402694 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic actions of Rad51 and Rad52 in recombination and DNA repair.Nature. 1998 Jan 22;391(6665):401-4. doi: 10.1038/34937. Nature. 1998. PMID: 9450758
-
RAD51 is required for the repair of plasmid double-stranded DNA gaps from either plasmid or chromosomal templates.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Feb;20(4):1194-205. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.4.1194-1205.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10648605 Free PMC article.
-
The RAD52 epistasis group in mammalian double strand break repair.Semin Immunol. 1997 Jun;9(3):181-8. doi: 10.1006/smim.1997.0067. Semin Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9200329 Review.
Cited by
-
NHEJ and HDR can occur simultaneously during gene integration into the genome of Aspergillus niger.Fungal Biol Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 5;11(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40694-024-00180-7. Fungal Biol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39103967 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Non-Thermal Plasma on Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 24;22(5):2247. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052247. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33668158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical-Genetic Interactions of Bacopa monnieri Constituents in Cells Deficient for the DNA Repair Endonuclease RAD1 Appear Linked to Vacuolar Disruption.Molecules. 2021 Feb 24;26(5):1207. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051207. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33668176 Free PMC article.
-
The N-terminus of RPA large subunit and its spatial position are important for the 5'->3' resection of DNA double-strand breaks.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 15;43(18):8790-800. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv764. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26227969 Free PMC article.
-
Collision of Trapped Topoisomerase 2 with Transcription and Replication: Generation and Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks with 5' Adducts.Genes (Basel). 2016 Jul 1;7(7):32. doi: 10.3390/genes7070032. Genes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27376333 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aguilera, A. 1995. Genetic evidence for different RAD52-dependent intrachromosomal recombination pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr. Genet. 27:298-305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

