Distinct regulation of salinity and genotoxic stress responses by Arabidopsis MAP kinase phosphatase 1
- PMID: 12456655
- PMCID: PMC136950
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf646
Distinct regulation of salinity and genotoxic stress responses by Arabidopsis MAP kinase phosphatase 1
Abstract
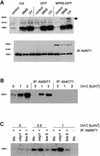
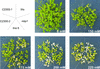
The Arabidopsis genome contains 20 genes encoding mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), which drastically outnumbers genes for their negative regulators, MAP kinase phosphatases (MKPs) (five at most). This contrasts sharply with genomes of other eukaryotes where the number of MAPKs and MKPs is approximately equal. MKPs may therefore play an important role in signal integration in plants, through concerted regulation of several MAPKs. Our previous studies identified Arabidopsis MKP1 and showed that its deficiency in the mkp1 mutant results in plant hypersensitivity to genotoxic stress. Here, we identify a set of MAPKs that interact with MKP1, and show that the activity level of one of these, MPK6, is regulated by MKP1 in vivo. Moreover, using expression profiling, we identified a specific group of genes that probably represent targets of MKP1 regulation. Surprisingly, the identity of these genes and interacting MAPKs suggested involvement of MKP1 in salt stress responses. Indeed, mkp1 plants have increased resistance to salinity. Thus MKP1 apparently plays a pivotal role in the integration and fine-tuning of plant responses to various environmental challenges.
Figures
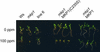



Similar articles
-
MAPK phosphatases--regulating the immune response.Nat Rev Immunol. 2007 Mar;7(3):202-12. doi: 10.1038/nri2035. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17318231 Review.
-
MAP kinase phosphatase 1 harbors a novel PTS1 and is targeted to peroxisomes following stress treatments.J Plant Physiol. 2015 May 1;179:12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2015.03.002. Epub 2015 Mar 12. J Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25817413
-
ATR and MKP1 play distinct roles in response to UV-B stress in Arabidopsis.Plant J. 2013 Mar;73(6):1034-43. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12095. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Plant J. 2013. PMID: 23237049
-
Phosphorylation and stabilization of Arabidopsis MAP kinase phosphatase 1 in response to UV-B stress.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 4;288(1):480-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.434654. Epub 2012 Nov 27. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23188831 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse physiological functions for dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases.J Cell Sci. 2006 Nov 15;119(Pt 22):4607-15. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03266. J Cell Sci. 2006. PMID: 17093265 Review.
Cited by
-
MAP Kinase Cascades in Arabidopsis Innate Immunity.Front Plant Sci. 2012 Jul 24;3:169. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00169. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22837762 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting phosphite-induced priming in Arabidopsis infected with Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis.Plant Physiol. 2012 May;159(1):286-98. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.194647. Epub 2012 Mar 9. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22408091 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and Genetic Interactions of Phospholipase D Alpha 1 and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 3 Affect Arabidopsis Stress Response.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Mar 18;10:275. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00275. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 30936884 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic dissection of Arabidopsis MAP kinase phosphatase 1-dependent PAMP-induced transcriptional responses.J Exp Bot. 2017 Nov 2;68(18):5207-5220. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx335. J Exp Bot. 2017. PMID: 29045691 Free PMC article.
-
Knockout of AtMKK1 enhances salt tolerance and modifies metabolic activities in Arabidopsis.Plant Signal Behav. 2013 May;8(5):e24206. doi: 10.4161/psb.24206. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Plant Signal Behav. 2013. PMID: 23511202 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albinsky D., Masson,J.E., Bogucki,A., Afsar,K., Vass,I., Nagy,F. and Paszkowski,J. (1999) Plant responses to genotoxic stress are linked to an ABA/salinity signaling pathway. Plant J., 17, 73–82.
-
- Apse M.P., Aharon,G.S., Snedden,W.A. and Blumwald,E. (1999) Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis. Science, 285, 1256–1258. - PubMed
-
- Asai T., Tena,G., Plotnikova,J., Willmann,M.R., Chiu,W.-L., Gomez-Gomez,L., Boller,T., Ausubel,F.M. and Sheen,J. (2002) MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature, 415, 977–983. - PubMed
-
- Bartel P.L. and Fields,S. (1995) Analyzing protein–protein interactions using two-hybrid system. Methods Enzymol., 254, 241–263. - PubMed
-
- Berset T., Fröhli Hoier,E., Battu,G., Canevascini,S. and Hajnal,A. (2001) Notch inhibition of RAS signaling through MAP kinase phosphatase LIP-1 during C.elegans vulval development. Science, 291, 1055–1058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

