The yeast pafl-rNA polymerase II complex is required for full expression of a subset of cell cycle-regulated genes
- PMID: 12455700
- PMCID: PMC126743
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.1.5.830-842.2002
The yeast pafl-rNA polymerase II complex is required for full expression of a subset of cell cycle-regulated genes
Abstract
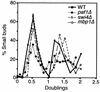
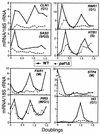
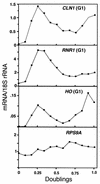
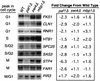
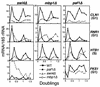
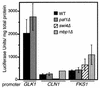
We have previously described an alternative form of RNA polymerase II in yeast lacking the Srb and Med proteins but including Pafl, Cdc73, Hprl, and Ccr4. The Pafl-RNA polymerase II complex (Paf1 complex) acts in the same pathway as the Pkc1-mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade and is required for full expression of many cell wall biosynthetic genes. The expression of several of these cell integrity genes, as well as many other Paf1-requiring genes identified by differential display and microarray analyses, is regulated during the cell cycle. To determine whether the Paf1 complex is required for basal or cyclic expression of these genes, we assayed transcript abundance throughout the cell cycle. We found that transcript abundance for a subset of cell cycle-regulated genes, including CLN1, HO, RNR1, and FAR1, is reduced from 2- to 13-fold in a paf1delta strain, but that this reduction is not promoter dependent. Despite the decreased expression levels, cyclic expression is still observed. We also examined the possibility that the Paf1 complex acts in the same pathway as either SBF (Swi4/Swi6) or MBF (Mbp1/Swi6), the partially redundant cell cycle transcription factors. Consistent with the possibility that they have overlapping essential functions, we found that loss of Paf1 is lethal in combination with loss of Swi4 or Swi6. In addition, overexpression of either Swi4 or Mbp1 suppresses some paf1delta phenotypes. These data establish that the Paf1 complex plays an important role in the essential regulatory pathway controlled by SBF and MBF.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phenotypic analysis of Paf1/RNA polymerase II complex mutations reveals connections to cell cycle regulation, protein synthesis, and lipid and nucleic acid metabolism.Mol Genet Genomics. 2002 Oct;268(2):272-85. doi: 10.1007/s00438-002-0752-8. Epub 2002 Sep 12. Mol Genet Genomics. 2002. PMID: 12395202
-
Ctr9, Rtf1, and Leo1 are components of the Paf1/RNA polymerase II complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Apr;22(7):1971-80. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.7.1971-1980.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11884586 Free PMC article.
-
A complex containing RNA polymerase II, Paf1p, Cdc73p, Hpr1p, and Ccr4p plays a role in protein kinase C signaling.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Feb;19(2):1056-67. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.2.1056. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 9891041 Free PMC article.
-
The evolution of a G1/S transcriptional network in yeasts.Curr Genet. 2018 Feb;64(1):81-86. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0726-3. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 28744706 Review.
-
Dancing the cell cycle two-step: regulation of yeast G1-cell-cycle genes by chromatin structure.Trends Biochem Sci. 2013 Sep;38(9):467-75. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2013.06.009. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Trends Biochem Sci. 2013. PMID: 23870664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The human PAF complex coordinates transcription with events downstream of RNA synthesis.Genes Dev. 2005 Jul 15;19(14):1668-73. doi: 10.1101/gad.1292105. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 16024656 Free PMC article.
-
Genic and global functions for Paf1C in chromatin modification and gene expression in Arabidopsis.PLoS Genet. 2008 Aug 22;4(8):e1000077. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000077. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18725930 Free PMC article.
-
Mpk1 MAPK association with the Paf1 complex blocks Sen1-mediated premature transcription termination.Cell. 2011 Mar 4;144(5):745-56. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.01.034. Cell. 2011. PMID: 21376235 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a role for histone H2B ubiquitylation in noncoding RNA 3'-end formation through mutational analysis of Rtf1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2011 Jun;188(2):273-89. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.128645. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Genetics. 2011. PMID: 21441211 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA polymerase-associated factor 1 complex (Paf1C) directly increases the elongation rate of RNA polymerase I and is required for efficient regulation of rRNA synthesis.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 7;285(19):14152-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.115220. Epub 2010 Mar 18. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20299458 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrews, B. J., and I. Herskowitz. 1989. The yeast SWI4 protein contains a motif present in developmental regulators and is part of a complex involved in cell-cycle-dependent transcription. Nature 342:830-833. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F. M., et al. (ed.). 1987. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York, N.Y.
-
- Betz, J. L., T. M. Washburn, S. E. Porter, C. L. Mueller, and J. A. Jaehning. Phenotypic analysis of Paf1/RNA polymerase II complex mutations reveals connections to cell cycle regulation, protein synthesis and lipid and nucleic acid metabolism. Mol. Genet. Genom., in press. - PubMed
-
- Breeden, L. L. 1997. Alpha-factor synchronization of budding yeast. Methods Enzymol. 283:332-341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

