Formation of extrachromosomal circles from telomeric DNA in Xenopus laevis
- PMID: 12446568
- PMCID: PMC1308322
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvf240
Formation of extrachromosomal circles from telomeric DNA in Xenopus laevis
Abstract
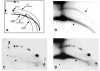
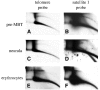
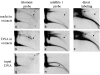
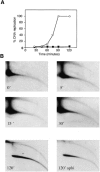
Instability and plasticity of telomeric DNA, which includes extrachromosomal DNA, are usually correlated with the absence of telomerase and with abnormal growth of mammalian cells. Here, we show the formation of extrachromosomal circular DNA of telomeric repeats (tel-eccDNA) during the development of Xenopus laevis. Tel-eccDNA is double-stranded relaxed circles composed of the vertebrate consensus telomeric repeats [TTAGGG](n). Its size varies from <2 to >20 kb and it comprises up to 10% of the total cellular telomere content of the early embryo (pre-MBT stage). The amount of tel-eccDNA is reduced in later developmental stages and in adult tissues. Using a cell-free system derived from Xenopus egg extracts, we show that tel-eccDNA can be formed de novo from the telomere chromosomal tracts of sperm nuclei and naked DNA in a replication-independent manner. These results reveal an unusual plasticity of telomeric DNA during normal development of Xenopus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel cell-free system reveals a mechanism of circular DNA formation from tandem repeats.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Jun 15;29(12):2542-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.12.2542. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11410662 Free PMC article.
-
Extrachromosomal circular DNA in eukaryotes: possible involvement in the plasticity of tandem repeats.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2009;124(3-4):327-38. doi: 10.1159/000218136. Epub 2009 Jun 25. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2009. PMID: 19556784 Review.
-
Regulated formation of extrachromosomal circular DNA molecules during development in Xenopus laevis.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Oct;19(10):6682-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.10.6682. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10490607 Free PMC article.
-
Recombination at long mutant telomeres produces tiny single- and double-stranded telomeric circles.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jun;25(11):4406-12. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.11.4406-4412.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15899847 Free PMC article.
-
Extrachromosomal circular DNA: a new potential role in cancer progression.J Transl Med. 2021 Jun 10;19(1):257. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02927-x. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34112178 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reactivation of chromosomally integrated human herpesvirus-6 by telomeric circle formation.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(12):e1004033. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004033. Epub 2013 Dec 19. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 24367281 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of cell-free eccDNAs in human plasma.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 8;7(1):10968. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11368-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28887493 Free PMC article.
-
Telomere rapid deletion regulates telomere length in Arabidopsis thaliana.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Mar;27(5):1706-15. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02059-06. Epub 2006 Dec 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17189431 Free PMC article.
-
Extrachromosomal circular DNA: biogenesis, structure, functions and diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Oct 2;7(1):342. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01176-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36184613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA is a co-factor for its own replication in Xenopus egg extracts.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(2):545-55. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq739. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 20861001 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

