Two chloroplastic viroids induce the accumulation of small RNAs associated with posttranscriptional gene silencing
- PMID: 12438638
- PMCID: PMC136683
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.24.13094-13096.2002
Two chloroplastic viroids induce the accumulation of small RNAs associated with posttranscriptional gene silencing
Abstract
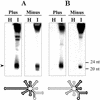
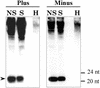
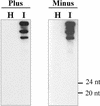
In plants, posttranscriptional gene silencing (PTGS) has been reported for cytoplasmic RNAs from endogenous nuclear genes, transgenes, viruses, and, recently, for a viroid with nuclear replication and accumulation. However, phenomena of this kind have not been described for mitochondrial or chloroplastic RNAs. Here we show that viroids that replicate and accumulate in the chloroplast are also targets of PTGS and this process may control viroid titer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Small RNAs containing the pathogenic determinant of a chloroplast-replicating viroid guide the degradation of a host mRNA as predicted by RNA silencing.Plant J. 2012 Jun;70(6):991-1003. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.04940.x. Epub 2012 Apr 4. Plant J. 2012. PMID: 22332758
-
Eggplant latent viroid is located in the chloroplasts and nuclei of eggplant infected cells.Virol J. 2024 Oct 15;21(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02530-8. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 39407314 Free PMC article.
-
Replicating Potato spindle tuber viroid mediates de novo methylation of an intronic viroid sequence but no cleavage of the corresponding pre-mRNA.RNA Biol. 2015;12(3):268-75. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1017216. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 25826660 Free PMC article.
-
Viroids and RNA silencing: mechanism, role in viroid pathogenicity and development of viroid-resistant plants.GM Crops. 2010 Mar-Apr;1(2):80-6. doi: 10.4161/gmcr.1.2.11871. GM Crops. 2010. PMID: 21865875 Review.
-
Viroids: how to infect a host and cause disease without encoding proteins.Biochimie. 2012 Jul;94(7):1474-80. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2012.02.020. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Biochimie. 2012. PMID: 22738729 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytopathic Effects Incited by Viroid RNAs and Putative Underlying Mechanisms.Front Plant Sci. 2013 Jan 7;3:288. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00288. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 23308076 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 6 delays accumulation and precludes meristem invasion of a viroid that replicates in the nucleus.J Virol. 2010 Mar;84(5):2477-89. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02336-09. Epub 2009 Dec 16. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20015979 Free PMC article.
-
Processing of nuclear viroids in vivo: an interplay between RNA conformations.PLoS Pathog. 2007 Nov;3(11):e182. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030182. PLoS Pathog. 2007. PMID: 18052530 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis thaliana has the enzymatic machinery for replicating representative viroid species of the family Pospiviroidae.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Apr 27;101(17):6792-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401090101. Epub 2004 Apr 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15096616 Free PMC article.
-
A viroid RNA with a specific structural motif inhibits chloroplast development.Plant Cell. 2007 Nov;19(11):3610-26. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.049775. Epub 2007 Nov 30. Plant Cell. 2007. PMID: 18055612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anandalakshmi, R., R. Marathe, X. Ge, J. M. Herr, Jr., C. Mau, A. Mallory, G. Pruss, L. Bowman, and V. B. Vance. 2000. A calmodulin-related protein that suppresses posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science 290:142-144. - PubMed
-
- Baulcombe, D. C. 2002. RNA silencing. Curr. Biol. 12:R82-R84. - PubMed
-
- Cogoni, C., and G. Macino. 2000. Post-transcriptional gene silencing across kingdoms. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 10:638-643. - PubMed
-
- Flores, R., J. W. Randles, M. Bar-Joseph, and T. O. Diener. 2000. Subviral agents: viroids, p. 1009-1024. In M. H. V. van Regenmortel et al. (ed.), Virus taxonomy, 7th Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Academic Press, San Diego, Calif.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

