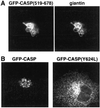
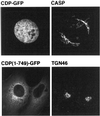
CASP, the alternatively spliced product of the gene encoding the CCAAT-displacement protein transcription factor, is a Golgi membrane protein related to giantin
- PMID: 12429822
- PMCID: PMC133590
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-06-0349
CASP, the alternatively spliced product of the gene encoding the CCAAT-displacement protein transcription factor, is a Golgi membrane protein related to giantin
Abstract
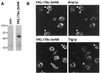
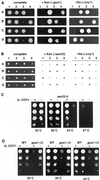
Large coiled-coil proteins are being found in increasing numbers on the membranes of the Golgi apparatus and have been proposed to function in tethering of transport vesicles and in the organization of the Golgi stack. Members of one class of Golgi coiled-coil protein, comprising giantin and golgin-84, are anchored to the bilayer by a single C-terminal transmembrane domain (TMD). In this article, we report the characterization of another mammalian coiled-coil protein, CASP, that was originally identified as an alternatively spliced product of the CUTL1 gene that encodes CCAAT-displacement protein (CDP), the human homologue of the Drosophila homeodomain protein Cut. We find that the Caenorhabditis elegans homologues of CDP and CASP are also generated from a single gene. CASP lacks the DNA binding motifs of CDP and was previously reported to be a nuclear protein. Herein, we show that it is in fact a Golgi protein with a C-terminal TMD and shares with giantin and golgin-84 a conserved histidine in its TMD. However, unlike these proteins, CASP has a homologue in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which we call COY1. Deletion of COY1 does not affect viability, but strikingly restores normal growth to cells lacking the Golgi soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor Gos1p. The conserved histidine is necessary for Coy1p's activity in cells lacking Gos1p, suggesting that the TMD of these transmembrane Golgi coiled-coil proteins is directly involved in their function.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of AtCASP, a plant transmembrane Golgi matrix protein.Plant Mol Biol. 2005 May;58(1):109-22. doi: 10.1007/s11103-005-4618-4. Plant Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16028120
-
Conserved juxtamembrane domains in the yeast golgin Coy1 drive assembly of a megadalton-sized complex and mediate binding to tethering and SNARE proteins.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jun 21;294(25):9690-9705. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008107. Epub 2019 May 9. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31073031 Free PMC article.
-
A novel Rab6-interacting domain defines a family of Golgi-targeted coiled-coil proteins.Curr Biol. 1999 Apr 8;9(7):381-4. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80167-5. Curr Biol. 1999. PMID: 10209123
-
Role of the multifunctional CDP/Cut/Cux homeodomain transcription factor in regulating differentiation, cell growth and development.Gene. 2001 May 30;270(1-2):1-15. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(01)00485-1. Gene. 2001. PMID: 11403998 Review.
-
Finding the Golgi: Golgin Coiled-Coil Proteins Show the Way.Trends Cell Biol. 2016 Jun;26(6):399-408. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2016.02.005. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Trends Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26972448 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic Insights into Disease Resistance in Sunflower (Helianthus annuus): Identifying Key Regions and Candidate Genes for Verticillium dahliae Resistance.Plants (Basel). 2024 Sep 14;13(18):2582. doi: 10.3390/plants13182582. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39339557 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of AtCASP, a plant transmembrane Golgi matrix protein.Plant Mol Biol. 2005 May;58(1):109-22. doi: 10.1007/s11103-005-4618-4. Plant Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16028120
-
Membrane tethering.F1000Prime Rep. 2014 Sep 4;6:74. doi: 10.12703/P6-74. eCollection 2014. F1000Prime Rep. 2014. PMID: 25343031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Golgin protein Coy1 functions in intra-Golgi retrograde transport and interacts with the COG complex and Golgi SNAREs.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Aug 9;28(20):2686-700. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-03-0137. Online ahead of print. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28794270 Free PMC article.
-
Retrograde vesicle transport in the Golgi.Protoplasma. 2012 Oct;249(4):943-55. doi: 10.1007/s00709-011-0361-7. Epub 2011 Dec 12. Protoplasma. 2012. PMID: 22160157 Review.
References
-
- Abe A, Emi N, Tanimoto M, Terasaki H, Marunouchi T, Saito H. Fusion of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta to a novel gene CEV14 in acute myelogenous leukemia after clonal evolution. Blood. 1997;90:4271–4277. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez C, Garcia-Mata R, Hauri HP, Sztul E. The p115-interactive proteins GM130 and giantin participate in endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi traffic. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:2693–2700. - PubMed
-
- Banfield DK, Lewis MJ, Pelham HR. A SNARE-like protein required for traffic through the Golgi complex. Nature. 1995;375:806–809. - PubMed
-
- Barberis A, Superti-Furga G, Busslinger M. Mutually exclusive interaction of the CCAAT-binding factor and of a displacement protein with overlapping sequences of a histone gene promoter. Cell. 1987;50:347–359. - PubMed
-
- Barr FA. A novel Rab6-interacting domain defines a family of Golgi-targeted coiled-coil proteins. Curr Biol. 1999;9:381–384. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

