Immediate and delayed VEGF-mediated NO synthesis in endothelial cells: role of PI3K, PKC and PLC pathways
- PMID: 12429574
- PMCID: PMC1573579
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704956
Immediate and delayed VEGF-mediated NO synthesis in endothelial cells: role of PI3K, PKC and PLC pathways
Abstract
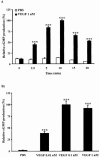
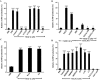
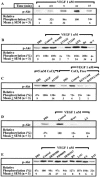
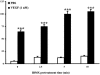
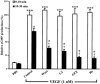
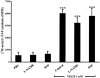
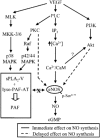
1. The mechanism(s) by which vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activation remain(s) unclear up to a certain extent. Therefore, we sought to evaluate the contribution of numerous pathways in VEGF-induced nitric oxide (NO) synthesis by measuring cGMP production. In addition, as VEGF induces the synthesis of NO and platelet-activating factor (PAF), we wanted to assess if the induction of PAF and NO is contributing to the synthesis of each other. 2. Herein, we show that a treatment of endothelial cells with a phospholipase C (PLC) inhibitor (U73122), a calmodulin antagonist (W-7) or with intracellular calcium chelators (EGTA/AM, BAPTA/AM) prevented VEGF-mediated eNOS Ser(1177)-phosphorylation and NO synthesis measured by cGMP production. 3. Pretreatment with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) (Wortmannin, LY294002) or protein kinase C (PKC) (GF109203X, Ro318220) inhibitors attenuated eNOS Ser(1177)-phosphorylation mediated by VEGF, but did not alter immediate (0-10 min) cGMP synthesis induced by VEGF, but abrogated by up to 84% the delayed (10-30 min) cGMP synthesis. 4. Pretreatment with PAF synthesis inhibitors or with PAF receptor antagonists did not abrogate neither eNOS Ser(1177)-phosphorylation nor cGMP synthesis mediated by VEGF. 5. In conclusion, VEGF induces an immediate cGMP synthesis through the PLC-Ca2+/CaM pathway, and that the induction of delayed cGMP synthesis implies Akt and PKC activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor induces protein kinase C (PKC)-dependent Akt/PKB activation and phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase-mediates PKC delta phosphorylation: role of PKC in angiogenesis.Cell Biol Int. 2002;26(9):751-9. doi: 10.1016/s1065-6995(02)90926-1. Cell Biol Int. 2002. PMID: 12377207
-
VEGF activates protein kinase C-dependent, but Ras-independent Raf-MEK-MAP kinase pathway for DNA synthesis in primary endothelial cells.Oncogene. 1999 Apr 1;18(13):2221-30. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202527. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10327068
-
Transactivation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor Flk-1/KDR is involved in sphingosine 1-phosphate-stimulated phosphorylation of Akt and endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (eNOS).J Biol Chem. 2002 Nov 8;277(45):42997-3001. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M204764200. Epub 2002 Sep 10. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12226078
-
Signal transduction of eNOS activation.Cardiovasc Res. 1999 Aug 15;43(3):532-41. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(99)00094-2. Cardiovasc Res. 1999. PMID: 10690325 Review.
-
Vascular endothelial dysfunction in aging: loss of Akt-dependent endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation and partial restoration by (R)-alpha-lipoic acid.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Dec;31(Pt 6):1447-9. doi: 10.1042/bst0311447. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 14641086 Review.
Cited by
-
Binding of the Andes Virus Nucleocapsid Protein to RhoGDI Induces the Release and Activation of the Permeability Factor RhoA.J Virol. 2021 Aug 10;95(17):e0039621. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00396-21. Epub 2021 Aug 10. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34133221 Free PMC article.
-
Arterial Stiffness Assessed by Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 26;20(15):3664. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153664. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31357449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of nitric oxide donors in the prevention and treatment of angiogenesis-inhibitor-induced hypertension.Angiogenesis. 2013 Apr;16(2):289-95. doi: 10.1007/s10456-012-9327-4. Epub 2012 Dec 1. Angiogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23203441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VEGF-mediated phosphorylation of eNOS regulates angioblast and embryonic endothelial cell proliferation.Dev Biol. 2013 Jan 1;373(1):163-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.10.020. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23103584 Free PMC article.
-
The matricellular protein thrombospondin-1 globally regulates cardiovascular function and responses to stress via CD47.Matrix Biol. 2012 Apr;31(3):162-9. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2012.01.005. Epub 2012 Jan 14. Matrix Biol. 2012. PMID: 22266027 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- BERNATCHEZ P.N., SOKER S., SIROIS M.G. Vascular endothelial growth factor effect on endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and platelet-activating factor synthesis is Flk-1-dependent. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:31047–31054. - PubMed
-
- BLIGH E.G., DYER W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959;37:911–917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

