Antigenic properties of the human immunodeficiency virus transmembrane glycoprotein during cell-cell fusion
- PMID: 12414953
- PMCID: PMC136862
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.23.12123-12134.2002
Antigenic properties of the human immunodeficiency virus transmembrane glycoprotein during cell-cell fusion
Abstract
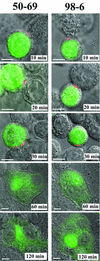
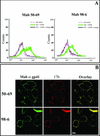
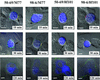
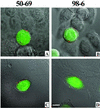
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) entry is triggered by interactions between a pair of heptad repeats in the gp41 ectodomain, which convert a prehairpin gp41 trimer into a fusogenic three-hairpin bundle. Here we examined the disposition and antigenic nature of these structures during the HIV-mediated fusion of HeLa cells expressing either HIV(HXB2) envelope (Env cells) or CXCR4 and CD4 (target cells). Cell-cell fusion, indicated by cytoplasmic dye transfer, was allowed to progress for various lengths of time and then arrested. Fusion intermediates were then examined for reactivity with various monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) against immunogenic cluster I and cluster II epitopes in the gp41 ectodomain. All of these MAbs produced similar staining patterns indicative of reactivity with prehairpin gp41 intermediates or related structures. MAb staining was seen on Env cells only upon exposure to soluble CD4, CD4-positive, coreceptor-negative cells, or stromal cell-derived factor-treated target cells. In the fusion system, the MAbs reacted with the interfaces of attached Env and target cells within 10 min of coculture. MAb reactivity colocalized with the formation of gp120-CD4-coreceptor tricomplexes after longer periods of coculture, although reactivity was absent on cells exhibiting cytoplasmic dye transfer. Notably, the MAbs were unable to inhibit fusion even when allowed to react with soluble-CD4-triggered or temperature-arrested antigens prior to initiation of the fusion process. In comparison, a broadly neutralizing antibody, 2F5, which recognizes gp41 antigens in the HIV envelope spike, was immunoreactive with free Env cells and Env-target cell clusters but not with fused cells. Notably, exposure of the 2F5 epitope required temperature-dependent elements of the HIV envelope structure, as MAb binding occurred only above 19 degrees C. Overall, these results demonstrate that immunogenic epitopes, both neutralizing and nonneutralizing, are accessible on gp41 antigens prior to membrane fusion. The 2F5 epitope appears to depend on temperature-dependent elements on prefusion antigens, whereas cluster I and cluster II epitopes are displayed by transient gp41 structures. Such findings have important implications for HIV vaccine approaches based on gp41 intermediates.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antigenic properties of the human immunodeficiency virus envelope during cell-cell fusion.J Virol. 2001 Nov;75(22):11096-105. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.22.11096-11105.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11602749 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 gp41 six-helix bundle formation occurs rapidly after the engagement of gp120 by CXCR4 in the HIV-1 Env-mediated fusion process.Biochemistry. 2001 Oct 16;40(41):12231-6. doi: 10.1021/bi0155596. Biochemistry. 2001. PMID: 11591141
-
HIV-1 gp41 Residues Modulate CD4-Induced Conformational Changes in the Envelope Glycoprotein and Evolution of a Relaxed Conformation of gp120.J Virol. 2018 Jul 31;92(16):e00583-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00583-18. Print 2018 Aug 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29875245 Free PMC article.
-
Progress towards the development of a HIV-1 gp41-directed vaccine.Curr HIV Res. 2004 Apr;2(2):193-204. doi: 10.2174/1570162043484933. Curr HIV Res. 2004. PMID: 15078183 Review.
-
The role of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoproteins in virus infection.J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 13;270(41):23883-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.41.23883. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7592573 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Specificity and 6-month durability of immune responses induced by DNA and recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara vaccines expressing HIV-1 virus-like particles.J Infect Dis. 2014 Jul 1;210(1):99-110. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu003. Epub 2014 Jan 7. J Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24403557 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Identification of the LWYIK motif located in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transmembrane gp41 protein as a distinct determinant for viral infection.J Virol. 2009 Jan;83(2):870-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01088-08. Epub 2008 Nov 5. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 18987155 Free PMC article.
-
Paring Down HIV Env: Design and Crystal Structure of a Stabilized Inner Domain of HIV-1 gp120 Displaying a Major ADCC Target of the A32 Region.Structure. 2016 May 3;24(5):697-709. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2016.03.005. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Structure. 2016. PMID: 27041594 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-gp41 antibodies cloned from HIV-infected patients with broadly neutralizing serologic activity.J Virol. 2010 May;84(10):5032-42. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00154-10. Epub 2010 Mar 10. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20219932 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamic landscape for antibody binding modulates antibody-mediated neutralization of West Nile virus.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Jun;7(6):e1002111. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002111. Epub 2011 Jun 30. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21738473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkhatib, G., C. Combadiere, C. C. Broder, Y. Feng, P. E. Kennedy, P. M. Murphy, and E. A. Berger. 1996. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1α, MIP-1β receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science 272:1955-1958. - PubMed
-
- Baker, K. A., R. E. Dutch, R. A. Lamb, and T. S. Jardetzky. 1999. Structural basis for paramyxovirus-mediated membrane fusion. Mol. Cell 3:309-319. - PubMed
-
- Buchacher, A., R. Predl, K. Strutzenberger, W. Steinfellner, A. Trkola, M. Purtscher, G. Gruber, C. Tauer, F. Steindl, A. Jungbauer, et al. 1994. Generation of human monoclonal antibodies against HIV-1 proteins; electrofusion and Epstein-Barr virus transformation for peripheral blood lymphocyte immortalization. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 10:359-369. - PubMed
-
- Bullough, P. A., F. M. Hughson, J. J. Skehel, and D. C. Wiley. 1994. Structure of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH of membrane fusion. Nature 371:37-43. - PubMed
-
- Cavacini, L. A., C. L. Emes, A. V. Wisnewski, J. Power, G. Lewis, D. Montefiori, and M. R. Posner. 1998. Functional and molecular characterization of human monoclonal antibody reactive with the immunodominant region of HIV type 1 glycoprotein 41. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 14:1271-1280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

