Effect of polyethylene glycol on the liquid-liquid phase transition in aqueous protein solutions
- PMID: 12391331
- PMCID: PMC137855
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.212507199
Effect of polyethylene glycol on the liquid-liquid phase transition in aqueous protein solutions
Abstract
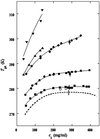
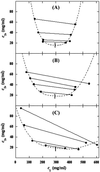
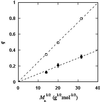
We have studied the effect of polyethylene glycol (PEG) on the liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) of aqueous solutions of bovine gammaD-crystallin (gammaD), a protein in the eye lens. We observe that the phase separation temperature increases with both PEG concentration and PEG molecular weight. PEG partitioning, which is the difference between the PEG concentration in the two coexisting phases, has been measured experimentally and observed to increase with PEG molecular weight. The measurements of both LLPS temperature and PEG partitioning in the ternary gammaD-PEG-water systems are used to successfully predict the location of the liquid-liquid phase boundary of the binary gammaD-water system. We show that our LLPS measurements can be also used to estimate the protein solubility as a function of the concentration of crystallizing agents. Moreover, the slope of the tie-lines and the dependence of LLPS temperature on polymer concentration provide a powerful and sensitive check of the validity of excluded volume models. Finally, we show that the increase of the LLPS temperature with PEG concentration is due to attractive protein-protein interactions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Observation of liquid-liquid phase separation for eye lens gammaS-crystallin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Feb 4;100(3):970-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.242746499. Epub 2003 Jan 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12529503 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between protein-polyethylene glycol (PEG) interactions and the effect of PEG on protein-protein interactions using the liquid-liquid phase transition.J Phys Chem B. 2007 Feb 8;111(5):1222-30. doi: 10.1021/jp065608u. J Phys Chem B. 2007. PMID: 17266278
-
Liquid-liquid phase transition of protein aqueous solutions isothermally induced by protein cross-linking.Langmuir. 2008 Mar 18;24(6):2799-807. doi: 10.1021/la703223f. Epub 2008 Jan 30. Langmuir. 2008. PMID: 18229962
-
Aqueous two-phase systems for protein separation: a perspective.J Chromatogr A. 2011 Dec 9;1218(49):8826-35. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2011.06.051. Epub 2011 Jun 21. J Chromatogr A. 2011. PMID: 21752387 Review.
-
Pharmaceutical Perspective on Opalescence and Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation in Protein Solutions.Mol Pharm. 2016 May 2;13(5):1431-44. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00937. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Mol Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27017836 Review.
Cited by
-
Controlled release of an anthrax toxin-neutralizing antibody from hydrolytically degradable polyethylene glycol hydrogels.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016 Jan;104(1):113-23. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.35545. Epub 2015 Aug 13. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016. PMID: 26223817 Free PMC article.
-
Utilizing polymer-conjugate albumin-based ultrafine gas bubbles in combination with ultra-high frequency radiations in drug transportation and delivery.RSC Adv. 2021 Oct 25;11(55):34440-34448. doi: 10.1039/d1ra04983f. eCollection 2021 Oct 25. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35494740 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Crowding Tunes Material States of Ribonucleoprotein Condensates.Biomolecules. 2019 Feb 19;9(2):71. doi: 10.3390/biom9020071. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 30791483 Free PMC article.
-
Phase Transitions in the Assembly and Function of Human miRISC.Cell. 2018 May 3;173(4):946-957.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.051. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Cell. 2018. PMID: 29576456 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation Enhances TDP-43 LCD Aggregation but Delays Seeded Aggregation.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 8;11(4):548. doi: 10.3390/biom11040548. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33917983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albertsson P. A., (1986) Partition of Cell Particles and Macromolecules (Wiley, New York).
-
- Abbott N. L., Blankschtein, D. & Hatton, T. A. (1991) Macromolecules 24, 4334-4348.
-
- McPherson A., (1999) Crystallization of Biological Macromolecules (Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press, Plainview, NY).
-
- Finet S. & Tardieu, A. (2001) J. Cryst. Growth 232, 40-49.
-
- Kulkarni A. M., Chatterjee, A. P., Schweizer, K. S. & Zukoski, C. F. (2000) J. Chem. Phys. 113, 9863-9873.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

