LPS-stimulated human gingival fibroblasts inhibit the differentiation of monocytes into osteoclasts through the production of osteoprotegerin
- PMID: 12390325
- PMCID: PMC1906523
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01990.x
LPS-stimulated human gingival fibroblasts inhibit the differentiation of monocytes into osteoclasts through the production of osteoprotegerin
Abstract
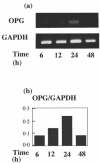
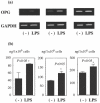
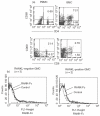
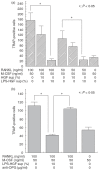
Periodontitis is an inflammatory bone disease caused by Gram-negative anaerobic bacteria, but the precise mechanism of bone destruction remains unknown. Activated T lymphocytes secrete receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) and support the differentiation of monocytes into mature osteoclasts. The purpose of this study was to examine the expression of RANKL and its inhibitor, osteoprotegerin (OPG), in inflamed gingival tissue and to clarify the role of human gingival fibroblasts (HGFs) in osteoclastogenesis regulated by RANKL. HGFs and gingival mononuclear cells (GMCs) were obtained from chronic periodontitis patients during routine periodontal surgery. Expression of OPG and RANKL mRNA in gingival tissue and HGFs was examined with RT-PCR. OPG production was measured using ELISA. Expression of RANKL, CD4, CD8 and CD69 on GMCs was determined by flow-cytometry using RANK-Fc fusion protein and the respective monoclonal antibodies. Osteoclastogenesis by RANKL was assayed by counting the number of tartarate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP)-positive cells after culturing human peripheral blood monocytes with recombinant human RANKL and macrophage-colony stimulating factor (M-CSF) for 10 days. OPG and RANKL mRNA were expressed in 80% (16/20) and 25% (5/20) of periodontitis lesions, respectively. OPG, but not RANKL, mRNA was expressed within HGFs. OPG mRNA expression and production by HGFs was augmented by LPS stimulation. All GMC samples expressed CD69, and two of five GMC samples expressed RANKL. The culture supernatant of LPS-stimulated gingival fibroblasts significantly reduced the number of TRAP positive cells generated by culturing monocytes with RANKL and M-CSF. The present study suggests that LPS-stimulated HGFs inhibit monocyte differentiation into osteoclasts through the production of OPG.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lipopolysaccharide stimulates expression of osteoprotegerin and receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand in periodontal ligament fibroblasts through the induction of interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha.Bone. 2004 Sep;35(3):629-35. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2004.04.023. Bone. 2004. PMID: 15336598
-
Protein kinase-A-dependent osteoprotegerin production on interleukin-1 stimulation in human gingival fibroblasts is distinct from periodontal ligament fibroblasts.Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 Dec;142(3):490-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02937.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16297161 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblastic stromal cells express receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand and support osteoclast differentiation.J Bone Miner Res. 2000 Aug;15(8):1459-66. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2000.15.8.1459. J Bone Miner Res. 2000. PMID: 10934644
-
Immune response: the key to bone resorption in periodontal disease.J Periodontol. 2005 Nov;76(11 Suppl):2033-41. doi: 10.1902/jop.2005.76.11-S.2033. J Periodontol. 2005. PMID: 16277573 Review.
-
The osteoclastogenic molecules RANKL and RANK are associated with periprosthetic osteolysis.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001 Aug;83(6):902-11. doi: 10.1302/0301-620x.83b6.10905. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001. PMID: 11521937 Review.
Cited by
-
Streptococcus mitis/human gingival fibroblasts co-culture: the best natural association in answer to the 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate release.APMIS. 2012 Feb;120(2):139-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2011.02828.x. Epub 2011 Oct 25. APMIS. 2012. PMID: 22229269 Free PMC article.
-
Oral mucosal dendritic cells and periodontitis: many sides of the same coin with new twists.Periodontol 2000. 2007;45:35-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2007.00222.x. Periodontol 2000. 2007. PMID: 17850447 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Role of periodontal pathogenic bacteria in RANKL-mediated bone destruction in periodontal disease.J Oral Microbiol. 2010 Nov 8;2. doi: 10.3402/jom.v2i0.5532. J Oral Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 21523224 Free PMC article.
-
AAV2/1-TNFR:Fc gene delivery prevents periodontal disease progression.Gene Ther. 2009 Mar;16(3):426-36. doi: 10.1038/gt.2008.174. Epub 2008 Dec 11. Gene Ther. 2009. PMID: 19078994 Free PMC article.
-
Role of osteoclasts in oral homeostasis and jawbone diseases.Oral Sci Int. 2020 Jan;18(1):14-27. doi: 10.1002/osi2.1078. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Oral Sci Int. 2020. PMID: 34220275 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suda T, Udagawa N, Takahashi N. The molecular mechanism of osteoclast differentiation and activation. Dentistry Japan. 2000;36:42–6.
-
- Kong Y-Y, Boyle WJ, Penninger JM. Osteoprotegerin ligand. a regulator of immune responses and bone physiology. Immunol Today. 2000;21:495–502. - PubMed
-
- Kong Y-Y, Yoshida H, Sarosi I, et al. OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature. 1999;397:315–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

