Continual production of phosphatidic acid by phospholipase D is essential for antigen-stimulated membrane ruffling in cultured mast cells
- PMID: 12388770
- PMCID: PMC129979
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e02-04-0213
Continual production of phosphatidic acid by phospholipase D is essential for antigen-stimulated membrane ruffling in cultured mast cells
Abstract
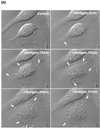
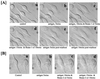
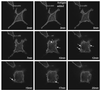
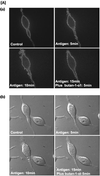
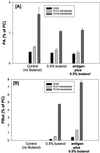
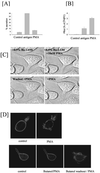
Phospholipase Ds (PLDs) are regulated enzymes that generate phosphatidic acid (PA), a putative second messenger implicated in the regulation of vesicular trafficking and cytoskeletal reorganization. Mast cells, when stimulated with antigen, show a dramatic alteration in their cytoskeleton and also release their secretory granules by exocytosis. Butan-1-ol, which diverts the production of PA generated by PLD to the corresponding phosphatidylalcohol, was found to inhibit membrane ruffling when added together with antigen or when added after antigen. Inhibition by butan-1-ol was completely reversible because removal of butan-1-ol restored membrane ruffling. Measurements of PLD activation by antigen indicate a requirement for continual PA production during membrane ruffling, which was maintained for at least 30 min. PLD1 and PLD2 are both expressed in mast cells and green fluorescent protein-tagged proteins were used to identify PLD2 localizing to membrane ruffles of antigen-stimulated mast cells together with endogenous ADP ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6). In contrast, green fluorescent protein-PLD1 localized to intracellular vesicles and remained in this location after stimulation with antigen. Membrane ruffling was independent of exocytosis of secretory granules because phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate increased membrane ruffling in the absence of exocytosis. Antigen or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate stimulation increased both PLD1 and PLD2 activity when expressed individually in RBL-2H3 cells. Although basal activity of PLD2-overexpressing cells is very high, membrane ruffling was still dependent on antigen stimulation. In permeabilized cells, antigen-stimulated phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate synthesis was dependent on both ARF6 and PA generated from PLD. We conclude that both activation of ARF6 by antigen and a continual PLD2 activity are essential for local phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate generation that regulates dynamic actin cytoskeletal rearrangements.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Endogenous phospholipase D2 localizes to the plasma membrane of RBL-2H3 mast cells and can be distinguished from ADP ribosylation factor-stimulated phospholipase D1 activity by its specific sensitivity to oleic acid.Biochem J. 2003 Jan 15;369(Pt 2):319-29. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021347. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12374567 Free PMC article.
-
Reversible bleb formation in mast cells stimulated with antigen is Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent and bleb size is regulated by ARF6.Biochem J. 2009 Dec 14;425(1):179-93. doi: 10.1042/BJ20091122. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19845506
-
Signalling role for ARF and phospholipase D in mast cell exocytosis stimulated by crosslinking of the high affinity FcepsilonR1 receptor.Mol Immunol. 2002 Sep;38(16-18):1277-82. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(02)00075-5. Mol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12217395 Review.
-
Activation of exocytosis by cross-linking of the IgE receptor is dependent on ADP-ribosylation factor 1-regulated phospholipase D in RBL-2H3 mast cells: evidence that the mechanism of activation is via regulation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate synthesis.Biochem J. 2000 Feb 15;346 Pt 1(Pt 1):63-70. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 10657240 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of phospholipase D and secretion in mast cells by protein kinase A and other protein kinases.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002 Jun;968:198-212. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04336.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002. PMID: 12119277 Review.
Cited by
-
Phospholipase D is involved in myogenic differentiation through remodeling of actin cytoskeleton.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Mar;16(3):1232-44. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-06-0459. Epub 2004 Dec 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15616193 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase D2 localizes to the plasma membrane and regulates angiotensin II receptor endocytosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Mar;15(3):1024-30. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-09-0673. Epub 2004 Jan 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 14718562 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Role of Phospholipase D in Bone Metabolism.J Bone Metab. 2023 May;30(2):117-125. doi: 10.11005/jbm.2023.30.2.117. Epub 2023 May 31. J Bone Metab. 2023. PMID: 37449345 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Key Phospholipids That Bind and Activate Atypical PKCs.Biomedicines. 2021 Jan 6;9(1):45. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9010045. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33419210 Free PMC article.
-
GEP100/BRAG2: activator of ADP-ribosylation factor 6 for regulation of cell adhesion and actin cytoskeleton via E-cadherin and alpha-catenin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jul 11;103(28):10672-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604091103. Epub 2006 Jun 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16807291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown FD, Thompson N, Saqib KM, Clark JM, Powner D, Thompson NT, Solari R, Wakelam MJO. Phospholipase D1 localizes to secretory granules and lysosomes and is plasma-membrane located on cellular stimulation. Curr Biol. 1998a;8:835–838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

