Visibly stressed: the role of eIF2, TIA-1, and stress granules in protein translation
- PMID: 12380690
- PMCID: PMC514820
- DOI: 10.1379/1466-1268(2002)007<0213:vstroe>2.0.co;2
Visibly stressed: the role of eIF2, TIA-1, and stress granules in protein translation
Abstract
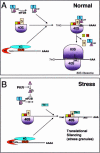
Eukaryotic cells express a family of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha (eIF2alpha) kinases (eg, PKR, PERK-PEK, GCN2, HRI) that are individually activated in response to distinct types of environmental stress. Phosphorylation of eIF2alpha by one or more of these kinases reduces the concentration of eIF2-guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-transfer ribonucleic acid for methionine (tRNA(Met)), the ternary complex that loads tRNA(Met) onto the small ribosomal subunit to initiate protein translation. When ternary complex levels are reduced, the related RNA-binding proteins TIA-1 and TIAR promote the assembly of a noncanonical preinitiation complex that lacks eIF2-GTP-tRNA(Met). The TIA proteins dynamically sort these translationally incompetent preinitiation complexes into discrete cytoplasmic domains known as stress granules (SGs). RNA-binding proteins that stabilize or destabilize messenger RNA (mRNA) are also recruited to SGs during stress. Thus, TIA-1 and TIAR act downstream of eIF2alpha phosphorylation to promote SG assembly and facilitate mRNA triage during stress. The role of the SG in the integration of translational efficiency, mRNA stability, and the stress response is discussed.
Figures
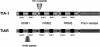

Similar articles
-
Evidence that ternary complex (eIF2-GTP-tRNA(i)(Met))-deficient preinitiation complexes are core constituents of mammalian stress granules.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Jan;13(1):195-210. doi: 10.1091/mbc.01-05-0221. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 11809833 Free PMC article.
-
Stress granules: sites of mRNA triage that regulate mRNA stability and translatability.Biochem Soc Trans. 2002 Nov;30(Pt 6):963-9. doi: 10.1042/bst0300963. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002. PMID: 12440955 Review.
-
Newcastle disease virus induces stable formation of bona fide stress granules to facilitate viral replication through manipulating host protein translation.FASEB J. 2017 Apr;31(4):1337-1353. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600980R. Epub 2016 Dec 23. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28011649
-
Stressful initiations.J Cell Sci. 2002 Aug 15;115(Pt 16):3227-34. doi: 10.1242/jcs.115.16.3227. J Cell Sci. 2002. PMID: 12140254
-
The role of host eIF2α in viral infection.Virol J. 2020 Jul 23;17(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-01362-6. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 32703221 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sequestration of RNA by grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella TIA1 is associated with its positive role in facilitating grass carp reovirus infection.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015 Oct;46(2):442-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2015.07.018. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26208752 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct binding properties of TIAR RRMs and linker region.RNA Biol. 2013 Apr;10(4):579-89. doi: 10.4161/rna.24341. Epub 2013 Apr 1. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23603827 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulation of the Small Heat Shock Protein B8 in Misfolding Protein Diseases Causing Motoneuronal and Muscle Cell Death.Front Neurosci. 2019 Aug 2;13:796. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00796. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31427919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress granule formation mediates the inhibition of colonic Hsp70 translation by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010 Apr;298(4):G481-92. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00234.2009. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20110459 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of tristetraprolin deadenylation by poly(A) binding protein.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008 Sep;295(3):G421-30. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00508.2007. Epub 2008 May 8. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18467502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barber GN. Host defense, viruses and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2001;8:113–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
