Jafrac2 is an IAP antagonist that promotes cell death by liberating Dronc from DIAP1
- PMID: 12356728
- PMCID: PMC129052
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdf530
Jafrac2 is an IAP antagonist that promotes cell death by liberating Dronc from DIAP1
Abstract
Members of the Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein (IAP) family are essential for cell survival in Drosophila and appear to neutralize the cell death machinery by binding to and ubiquitylating pro-apoptotic caspases. Cell death is triggered when "Reaper-like" proteins bind to IAPs and liberate caspases from IAPs. We have identified the thioredoxin peroxidase Jafrac2 as an IAP-interacting protein in Drosophila cells that harbours a conserved N-terminal IAP-binding motif. In healthy cells, Jafrac2 resides in the endoplasmic reticulum but is rapidly released into the cytosol following induction of apoptosis. Mature Jafrac2 interacts genetically and biochemically with DIAP1 and promotes cell death in tissue culture cells and the Drosophila developing eye. In common with Rpr, Jafrac2-mediated cell death is contingent on DIAP1 binding because mutations that abolish the Jafrac2-DIAP1 interaction suppress the eye phenotype caused by Jafrac2 expression. We show that Jafrac2 displaces Dronc from DIAP1 by competing with Dronc for the binding of DIAP1, consistent with the idea that Jafrac2 triggers cell death by liberating Dronc from DIAP1-mediated inhibition.
Figures
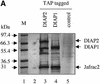



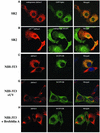



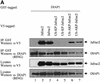




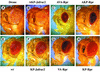
Similar articles
-
The DIAP1 RING finger mediates ubiquitination of Dronc and is indispensable for regulating apoptosis.Nat Cell Biol. 2002 Jun;4(6):445-50. doi: 10.1038/ncb799. Nat Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12021771
-
IAP-antagonists exhibit non-redundant modes of action through differential DIAP1 binding.EMBO J. 2003 Dec 15;22(24):6642-52. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg617. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 14657035 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila caspase DRONC is regulated by DIAP1.EMBO J. 2000 Feb 15;19(4):598-611. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.4.598. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 10675329 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of apoptosis in Drosophila.Cell Death Differ. 2008 Jul;15(7):1132-8. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2008.50. Epub 2008 Apr 25. Cell Death Differ. 2008. PMID: 18437164 Review.
-
Destabilizing influences in apoptosis: sowing the seeds of IAP destruction.Cell. 2002 Jun 28;109(7):793-6. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00802-4. Cell. 2002. PMID: 12110175 Review.
Cited by
-
Fork head controls the timing and tissue selectivity of steroid-induced developmental cell death.J Cell Biol. 2007 Mar 12;176(6):843-52. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200611155. Epub 2007 Mar 5. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17339378 Free PMC article.
-
Apical deficiency triggers JNK-dependent apoptosis in the embryonic epidermis of Drosophila.Development. 2011 Jul;138(14):3021-31. doi: 10.1242/dev.059980. Development. 2011. PMID: 21693518 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of peroxiredoxin 4 on fly physiology is a complex interplay of antioxidant and signaling functions.FASEB J. 2013 Apr;27(4):1426-38. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-214106. Epub 2012 Dec 27. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23271054 Free PMC article.
-
The protein structures that shape caspase activity, specificity, activation and inhibition.Biochem J. 2004 Dec 1;384(Pt 2):201-32. doi: 10.1042/BJ20041142. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15450003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A fluorescent reporter of caspase activity for live imaging.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 16;105(37):13901-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0806983105. Epub 2008 Sep 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18779587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen P., Nordstrom,W., Gish,B. and Abrams,J.M. (1996) grim, a novel cell death gene in Drosophila. Genes Dev., 10, 1773–1782. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein J.C., Nigel,N.J., Juin,P., Evan,G. and Green,D.R. (2000) The coordinated release of cytochrome c during apoptosis is rapid, complete and kinetically invariant. Nat. Cell Biol., 2, 156–162. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

