CARPEL FACTORY, a Dicer homolog, and HEN1, a novel protein, act in microRNA metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 12225663
- PMCID: PMC5137372
- DOI: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)01017-5
CARPEL FACTORY, a Dicer homolog, and HEN1, a novel protein, act in microRNA metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
Background: In metazoans, microRNAs, or miRNAs, constitute a growing family of small regulatory RNAs that are usually 19-25 nucleotides in length. They are processed from longer precursor RNAs that fold into stem-loop structures by the ribonuclease Dicer and are thought to regulate gene expression by base pairing with RNAs of protein-coding genes. In Arabidopsis thaliana, mutations in CARPEL FACTORY (CAF), a Dicer homolog, and those in a novel gene, HEN1, result in similar, multifaceted developmental defects, suggesting a similar function of the two genes, possibly in miRNA metabolism.
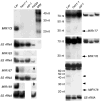
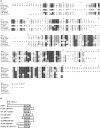
Results: To investigate the potential functions of CAF and HEN1 in miRNA metabolism, we aimed to isolate miRNAs from Arabidopsis and examine their accumulation during plant development in wild-type plants and in hen1-1 and caf-1 mutant plants. We have isolated 11 miRNAs, some of which have potential homologs in tobacco, rice, and maize. The putative precursors of these miRNAs have the capacity to form stable stem-loop structures. The accumulation of these miRNAs appears to be spatially or temporally controlled in plant development, and their abundance is greatly reduced in caf-1 and hen1-1 mutants. HEN1 homologs are found in bacterial, fungal, and metazoan genomes.
Conclusions: miRNAs are present in both plant and animal kingdoms. An evolutionarily conserved mechanism involving a protein, known as Dicer in animals and CAF in Arabidopsis, operates in miRNA metabolism. HEN1 is a new player in miRNA accumulation in Arabidopsis, and HEN1 homologs in metazoans may have a similar function. The developmental defects associated with caf-1 and hen1-1 mutations and the patterns of miRNA accumulation suggest that miRNAs play fundamental roles in plant development.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functional mapping of the plant small RNA methyltransferase: HEN1 physically interacts with HYL1 and DICER-LIKE 1 proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Mar 11;43(5):2802-12. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv102. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25680966 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in plants.Genes Dev. 2002 Jul 1;16(13):1616-26. doi: 10.1101/gad.1004402. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 12101121 Free PMC article.
-
Posttranscriptional gene silencing is not compromised in the Arabidopsis CARPEL FACTORY (DICER-LIKE1) mutant, a homolog of Dicer-1 from Drosophila.Curr Biol. 2003 Feb 4;13(3):236-40. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00010-1. Curr Biol. 2003. PMID: 12573220
-
MicroRNA biogenesis and function in plants.FEBS Lett. 2005 Oct 31;579(26):5923-31. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.07.071. Epub 2005 Aug 9. FEBS Lett. 2005. PMID: 16144699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep sequencing from hen1 mutants to identify small RNA 3' modifications.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2012;77:213-9. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2013.77.014779. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2012. PMID: 23393108 Review.
Cited by
-
Arabidopsis proline-rich protein important for development and abiotic stress tolerance is involved in microRNA biogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 30;109(44):18198-203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216199109. Epub 2012 Oct 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23071326 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs inhibit the translation of target mRNAs on the endoplasmic reticulum in Arabidopsis.Cell. 2013 Apr 25;153(3):562-74. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.04.005. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23622241 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNA and degradome sequencing reveals microRNAs and their targets involved in tomato pedicel abscission.Planta. 2015 Oct;242(4):963-84. doi: 10.1007/s00425-015-2318-0. Epub 2015 May 29. Planta. 2015. PMID: 26021606
-
Distinct and cooperative activities of HESO1 and URT1 nucleotidyl transferases in microRNA turnover in Arabidopsis.PLoS Genet. 2015 Apr 30;11(4):e1005119. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005119. eCollection 2015 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25928405 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: Potential Targets for Developing Stress-Tolerant Crops.Life (Basel). 2021 Mar 28;11(4):289. doi: 10.3390/life11040289. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33800690 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hamilton AJ, Baulcombe DC. A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science. 1999;286:950–952. - PubMed
-
- Zamore PD. Ancient pathways programmed by small RNAs. Science. 2002;296:1265–1269. - PubMed
-
- Plasterk RH. RNA silencing: the genome’s immune system. Science. 2002;296:1263–1265. - PubMed
-
- Zamore PD, Tuschl T, Sharp P, Bartel D. RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell. 2000;101:25–33. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature. 2001;409:363–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

