Extrasynaptic alpha 7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expression in developing neurons is regulated by inputs, targets, and activity
- PMID: 12223564
- PMCID: PMC6758097
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-18-08101.2002
Extrasynaptic alpha 7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expression in developing neurons is regulated by inputs, targets, and activity
Abstract
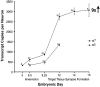
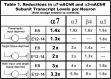
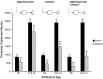
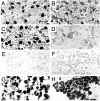
Alpha7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) are widely expressed in the vertebrate nervous system. alpha7-nAChR functions include postsynaptic transmission, modulating neurotransmitter release, reinforcing nicotine addiction, and a role in neurological disorders, such as schizophrenia and Alzheimer's disease. In chick parasympathetic ciliary ganglion (CG) neurons, alpha7-nAChRs are excluded from the synapse and localize perisynaptically. Despite their extrasynaptic distribution, the highly Ca2+-permeable alpha7-nAChRs have important synapse-related Ca2+-dependent signaling functions in the CG. We show here that the synaptic partners regulate alpha7-nAChR expression during synapse formation in embryonic CG neurons in situ. The absence of inputs and target tissues cause reductions in alpha7-nAChR mRNA and protein levels that primarily resemble those seen for synaptic alpha3-nAChRs. However, there is a difference in their regulation. alpha7-nAChR levels are downregulated by reduced activity, whereas alpha3-nAChR levels are not. We propose that the activity-dependent regulation of extrasynaptic alpha7-nAChR levels may be an important mechanism for postsynaptic CG neurons to detect changes in presynaptic activity levels and respond with Ca2+-dependent plasticity changes in gene expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and trkB signaling in parasympathetic neurons: relevance to regulating alpha7-containing nicotinic receptors and synaptic function.J Neurosci. 2004 May 5;24(18):4340-50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0055-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15128848 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral mobility of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on neurons is determined by receptor composition, local domain, and cell type.J Neurosci. 2010 Jun 30;30(26):8841-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6236-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20592206 Free PMC article.
-
α7-Containing and non-α7-containing nicotinic receptors respond differently to spillover of acetylcholine.J Neurosci. 2011 Oct 19;31(42):14920-30. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3400-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22016525 Free PMC article.
-
The alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in neuronal plasticity.Mol Neurobiol. 1999 Aug;20(1):1-16. doi: 10.1007/BF02741361. Mol Neurobiol. 1999. PMID: 10595869 Review.
-
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in autonomic ganglia.Auton Neurosci. 2002 Apr 18;97(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/s1566-0702(01)00386-1. Auton Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12036180 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional mapping and Ca2+ regulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor channels in rat hippocampal CA1 neurons.J Neurosci. 2003 Oct 8;23(27):9024-31. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-27-09024.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14534236 Free PMC article.
-
A null mutation for the alpha3 nicotinic acetylcholine (ACh) receptor gene abolishes fast synaptic activity in sympathetic ganglia and reveals that ACh output from developing preganglionic terminals is regulated in an activity-dependent retrograde manner.J Neurosci. 2005 Sep 14;25(37):8555-66. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1983-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16162937 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and trkB signaling in parasympathetic neurons: relevance to regulating alpha7-containing nicotinic receptors and synaptic function.J Neurosci. 2004 May 5;24(18):4340-50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0055-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15128848 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of Human α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor by α-Conotoxin ImI Dendrimer: Insight from Computational Simulations.Mar Drugs. 2019 May 23;17(5):303. doi: 10.3390/md17050303. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31126085 Free PMC article.
-
The dual-gate model for pentameric ligand-gated ion channels activation and desensitization.J Physiol. 2018 May 15;596(10):1873-1902. doi: 10.1113/JP275100. Epub 2018 Apr 17. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29484660 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
