Identification of Epstein-Barr virus strain variants in hairy leukoplakia and peripheral blood by use of a heteroduplex tracking assay
- PMID: 12208943
- PMCID: PMC136523
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.19.9645-9656.2002
Identification of Epstein-Barr virus strain variants in hairy leukoplakia and peripheral blood by use of a heteroduplex tracking assay
Abstract
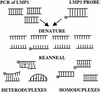
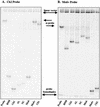
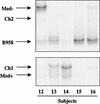
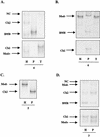
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) strains can be distinguished by specific sequence variations in the LMP1 gene. In this study, a heteroduplex tracking assay (HTA) specific for LMP1 was developed to precisely identify the prototypic undeleted strain B958, other undeleted strains (Ch2, AL, NC, and Med-), and strains with the 30-bp deletion (Med+ and Ch1). This technique also provides an estimate of the relative abundance of strains in patient samples. In this study, EBV strains were identified in 25 hairy leukoplakia (HLP) biopsies and six matched peripheral blood samples and throat washes with the LMP1-HTA. To investigate the relationship of the virus found in the peripheral blood to that in the HLP lesion, the strain variants in the peripheral blood B lymphocytes and those present within the epithelial cells in the HLP lesion and in throat washes were identified. In many of the subjects, compartmental differences in the EBV strain profiles in the oral cavity and peripheral blood were readily apparent. The throat wash specimens usually had a strain profile similar to that within the corresponding HLP sample, which was distinct from the strain profile detected in the peripheral blood. These analyses reveal that the nature of EBV infection can be very dynamic, with changes in relative strain abundance over time as well as the appearance of new strains. The patterns of abundance in the blood and oral cavity provide evidence for compartmentalization and for the transmission of strains between the blood and oropharynx.
Figures


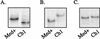
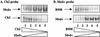

Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus coinfection and recombination in non-human immunodeficiency virus-associated oral hairy leukoplakia.J Infect Dis. 1995 May;171(5):1122-30. doi: 10.1093/infdis/171.5.1122. J Infect Dis. 1995. PMID: 7751686
-
Epstein-Barr virus intrastrain recombination in oral hairy leukoplakia.J Virol. 1994 Dec;68(12):7909-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.68.12.7909-7917.1994. J Virol. 1994. PMID: 7966581 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription of Epstein-Barr virus latent cycle genes in oral hairy leukoplakia.Virology. 1998 Aug 15;248(1):53-65. doi: 10.1006/viro.1998.9268. Virology. 1998. PMID: 9705255
-
Epstein-Barr virus strains and variations: Geographic or disease-specific variants?J Med Virol. 2017 Mar;89(3):373-387. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24633. Epub 2016 Dec 5. J Med Virol. 2017. PMID: 27430663 Review.
-
Epstein-Barr virus in oral diseases.J Periodontal Res. 2006 Aug;41(4):235-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2006.00865.x. J Periodontal Res. 2006. PMID: 16827715 Review.
Cited by
-
LMP1 strain variants: biological and molecular properties.J Virol. 2006 Jul;80(13):6458-68. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00135-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16775333 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoinformatics Approach to Design Novel Subunit Vaccine against the Epstein-Barr Virus.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0115122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01151-22. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36094198 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary shedding of Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus in people infected or not by human immunodeficiency virus 1.Clin Oral Investig. 2012 Apr;16(2):659-64. doi: 10.1007/s00784-011-0548-5. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Clin Oral Investig. 2012. PMID: 22186943
-
Sequencing-based detection of low-frequency human immunodeficiency virus type 1 drug-resistant mutants by an RNA/DNA heteroduplex generator-tracking assay.J Virol. 2004 Jul;78(13):7112-23. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.13.7112-7123.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15194787 Free PMC article.
-
Compartmentalization and transmission of multiple epstein-barr virus strains in asymptomatic carriers.J Virol. 2003 Feb;77(3):1840-7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.3.1840-1847.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12525618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Hamid, M., J. J. Chen, N. Constantine, M. Massoud, and N. Raab-Traub. 1992. EBV strain variation: geographical distribution and relation to disease state. Virology 190:168-175. - PubMed
-
- Anagnostopoulos, I., M. Hummel, C. Kreschel, and H. Stein. 1995. Morphology, immunophenotype, and distribution of latently and/or productively Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells in acute infectious mononucleosis: implications for the interindividual infection route of Epstein-Barr virus. Blood 85:744-750. - PubMed
-
- Babcock, G. J., L. L. Decker, M. Volk, and D. A. Thorley-Lawson. 1998. EBV persistence in memory B cells in vivo. Immunity 9:395-404. - PubMed
-
- Berger, C., D. van Baarle, M. J. Kersten, M. R. Klein, A. S. Al-Homsi, B. Dunn, C. McQuain, R. van Oers, and H. Knecht. 1999. Carboxy terminal variants of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 during long-term human immunodeficiency virus infection: reliable markers for individual strain identification. J. Infect. Dis. 179:240-244. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia, K., A. Raj, M. I. Guitierrez, J. G. Judde, G. Spangler, H. Venkatesh, and I. T. Magrath. 1996. Variation in the sequence of Epstein Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 in normal peripheral blood lymphocytes and in Burkitt's lymphomas. Oncogene 13:177-181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

